Graphic design is the art of communicating visually, where ideas and messages transform into captivating images, with 73% of companies investing in design to differentiate their brand (Adobe, 2018).
Whether designing a logo, a website, or a simple poster, understanding the fundamental graphic design elements is essential for success. These elements are the building blocks that, when skillfully combined, create visually appealing and effective designs.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the foundational elements of graphic design, starting with the core ones and how they interact to form the basis of compelling visuals.
Let’s get started!
Eduma – Education WordPress Theme
We provide an amazing WordPress theme with fast and responsive designs. Let’s find out!
Why Graphic Design Elements Matter in Branding and Marketing

Before listing the elements, it is important to understand why they matter in real-world design. Graphic design elements serve as the foundation of every visual composition. Just as words form the foundation of communication, design elements build the language of visuals.
By mastering the elements of design, you can:
- Communicate with clarity – Deliver messages that are easy to understand.
- Create visual impact – Design graphics that capture attention.
- Build strong brand identity – Shape consistent visuals that reflect your values.
- Guide user experience – Direct the viewer’s eyes through information naturally.
- Stand out in competition – Make your work more professional and memorable.
What Are The Basic Graphic Design Elements?
Line
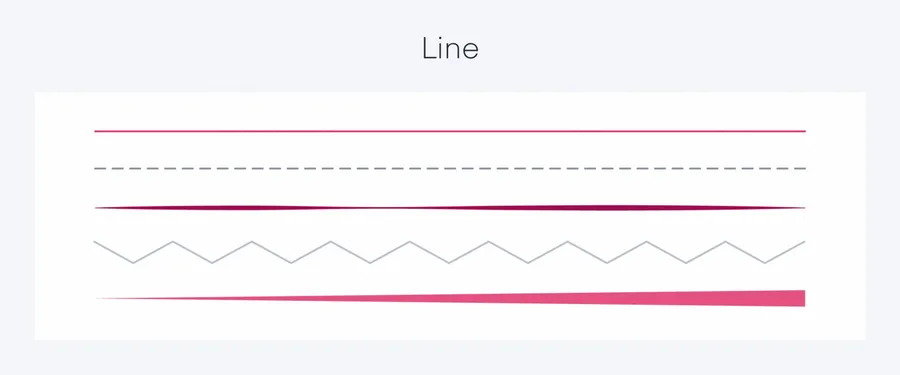
A line is more than just a mark on a page.
They’re the pathways that guide our eyes, create movement, and evoke emotions. Straight lines convey stability, while curved lines suggest fluidity.
A diagonal line might imply action, whereas a vertical line signifies strength.
Think of the iconic Nike swoosh – a simple, dynamic line that embodies the brand’s energy and movement.
It’s one of the basic graphic design elements you should know.
Role in Design:
- Structure and Organization: Lines create the underlying framework of a design, guiding the viewer’s eye and dividing space.
- Movement and Direction: Lines can suggest motion, leading the eye from one element to another.
- Emotion and Expression: Different line styles generate various emotions. Straight lines often feel strong and stable, while curved lines can be graceful or playful.
- Texture and Pattern: You can make complex patterns or visual textures with lines.
Color
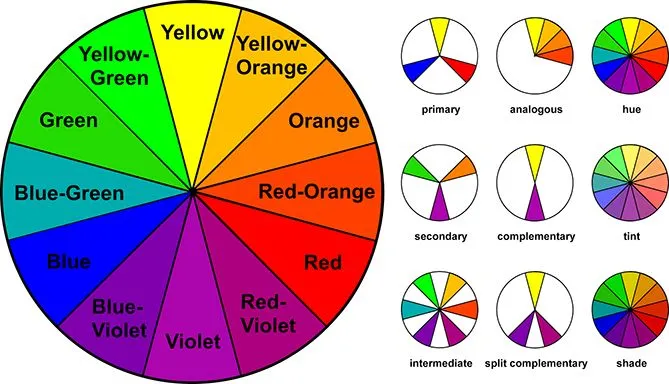
Color is the visual perception of light reflected or emitted from an object.
It’s characterized by hue (the name of the color, like red or blue), saturation (the intensity or purity of the color), and value (the lightness or darkness of the color).
Role in Design:
- Mood and Atmosphere: Colors evoke powerful emotions and set the overall tone of a design. Warm colors (reds, oranges, yellows) often feel energetic and exciting, while cool colors (blues, greens, purples) can be calming or mysterious.
- Emphasis and Contrast: In a design, color can be employed to draw attention to key components or to contrast different areas.
- Symbolism and Meaning: Colors often have cultural associations and symbolic meanings that can be leveraged in design.
- Realism and Depth: Color can be used to create the illusion of three-dimensionality and make objects appear more realistic.
Texture

Texture is among the famous elements of graphic design.
It’s the tactile quality of a surface or the visual representation of that quality. It can be physical (the actual feel of a material) or visual (the illusion of texture created by lines, shapes, or colors).
Role in Design:
- Visual Interest: Texture adds depth and complexity to a design, making it more engaging to the eye.
- Realism and Tactility: Texture can create the illusion of different materials, like fabric, wood, or stone. Poster templates often use texture overlays to add depth and make print or digital designs stand out.
- Contrast and Emphasis: Texture can be used to create contrast with other elements in a design, making certain areas stand out.
- Mood and Atmosphere: Different textures can evoke different feelings, like roughness, smoothness, or softness.
Shape

A shape is a self-contained, two-dimensional area defined by lines, color, or texture.
Shapes can be geometric (circles, squares, triangles) or organic (freeform, irregular).
Role in Design:
- Building Blocks: Shapes are fundamental components for creating visual elements and illustrations.
- Symbolism and Meaning: Certain shapes carry universal meanings (e.g., circles for unity, and triangles for stability) that can be used intentionally.
- Visual Hierarchy: Shapes can be used to organize information and guide the viewer’s eye.
- Balance and Composition: The arrangement of shapes can create a sense of harmony or tension.
Space

Space is listed as one of the core graphic design elements.
It refers to the areas around and between elements in a design.
It can be positive (the filled areas) or negative (the empty areas).
Role in Design:
- Breathing Room: Negative space gives elements room to “breathe,” preventing a design from feeling cluttered.
- Focus and Emphasis: Negative space can be used to draw attention to specific elements.
- Elegance and Sophistication: Thoughtful use of space often creates a clean, polished look.
- Balance and Composition: The distribution of positive and negative space greatly impacts the overall feel of a design.
Typography

Typography refers to the arrangement and style of letters, numbers, and symbols used in visual communication.
It includes the selection of typefaces (fonts), their sizes, spacing, and the overall layout of text.
Role in Design:
- Communication: Typography is essential for conveying information and ideas effectively.
- Tone and Personality: Different typefaces (fonts) evoke different moods and associations.
- Hierarchy and Organization: Typography can establish a visual hierarchy by using different sizes, weights, and styles of type.
- Visual Interest: Creative typography can become an artistic element in itself, adding visual appeal to a design.
Form
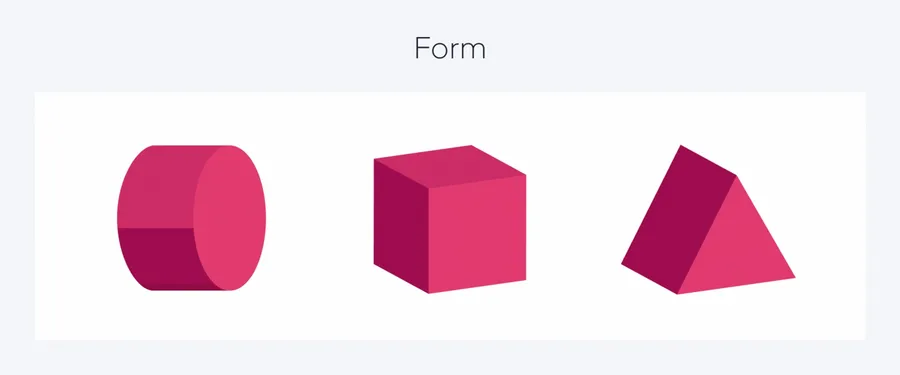
Form refers to the three-dimensional aspect of an object or design.
It’s the illusion of depth, volume, and mass-created within a two-dimensional space.
Role in Design:
- Realism and Depth: Form gives designs a sense of dimensionality, making elements appear more tangible and realistic.
- Visual Interest: The interplay of light and shadow on a form can create captivating visual effects.
- Emphasis and Hierarchy: Form can be used to make certain elements stand out or recede into the background, establishing a visual hierarchy.
- Mood and Atmosphere: Different forms can evoke different feelings, such as stability, lightness, or dynamism.
Size

Size is the physical dimensions (height and width) of a design element or the relative proportions of different elements within a design.
Role in Design:
- Emphasis and Focus: Larger elements naturally attract more attention, allowing designers to highlight specific points.
- Hierarchy and Organization: Varying sizes of elements create a visual order, guiding the viewer through the design.
- Balance and Proportion: The relative sizes of elements contribute to a harmonious and balanced composition.
Value

Value refers to the lightness or darkness of a color or tone.
It’s a crucial aspect of creating contrast and depth within a design.
Value can range from pure white (highest value) to pure black (lowest value), with various shades of gray in between.
Role in Design:
- Form and Dimension: Value is essential for creating the illusion of form and three-dimensionality. It can make objects appear to recede or advance in space.
- Contrast and Emphasis: Contrasting values can focus attention on specific elements or areas of a design.
- Mood and Atmosphere: Lighter values often show a sense of airiness and optimism, while darker values can feel more dramatic or mysterious.
- Readability: In typography, value contrast between text and background is crucial for legibility.
Contrast

Contrast is the degree of visual difference between graphic design elements.
Color, size, shape, texture, and other visual attributes can all contribute to contrast.
Role in Design:
- Readability: Sufficient contrast between text and background ensures that words are easy to read.
- Visual Interest: Contrast makes designs more dynamic and engaging.
- Emphasis: High contrast between elements can highlight specific parts of a design.
- Organization: Contrast can be used to group or separate elements, aiding in the overall structure of a design.
Imagery
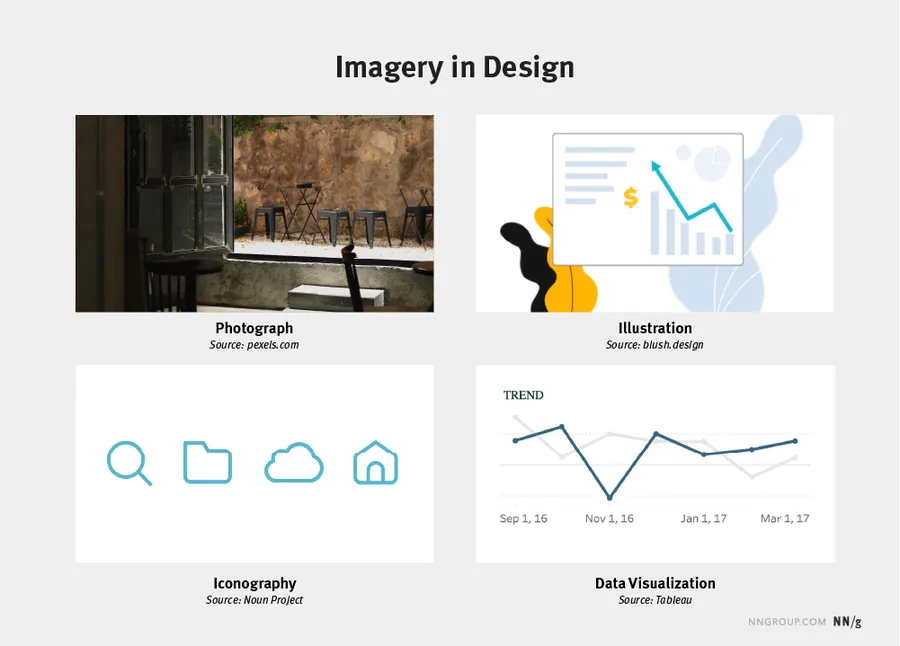
Imagery encompasses all visual elements used in a design, including photographs, illustrations, icons, and symbols.
Role in Design:
- Storytelling and Communication: Imagery is a powerful tool for conveying complex ideas and emotions.
- Engagement and Appeal: Compelling imagery can capture and hold the viewer’s attention.
- Brand Identity: Imagery can be used to create a memorable visual identity for a brand or product.
- Mood and Atmosphere: The choice of imagery can significantly impact the overall tone of a design.
How to Apply Graphic Design Elements Effectively
Understanding elements is not enough. The true skill lies in combining them effectively. A successful design balances line, color, shape, and typography while using space, value, and contrast to enhance readability and flow.
Tips for applying design elements:
- Use contrasting colors for visibility and emphasis.
- Maintain typographic hierarchy for clarity.
- Apply negative space to avoid overcrowding.
- Choose textures and imagery that match brand identity.
- Keep size and proportion consistent for balance.
Graphic Design Elements vs Principles of Design
While elements of design are the building blocks, the principles of design are the rules for arranging them.
| Design Elements | Design Principles |
|---|---|
| Line, Shape, Color, Texture, Space, Typography, Form, Size, Value, Contrast, Imagery | Balance, Alignment, Proportion, Rhythm, Emphasis, Unity |
Both must work together for successful design.
Conclusion
Mastering the basic elements of graphic design is essential for anyone who wants to create professional, effective, and memorable visuals. From lines and shapes to typography and contrast, each element contributes to the overall communication of your design.
Design is a continuous learning process. By practicing and experimenting with these elements, you will develop stronger creative skills and produce designs that engage, inspire, and convert.
Conclusion
Understanding and skillfully applying the elements of graphic design is a journey, not a destination. It’s about constantly experimenting, learning, and refining your skills. Whether you’re designing a simple social media graphic or a complex website, these fundamentals will serve as your trusty toolkit. Embrace them, and watch your designs transform.
FAQs of Basic Graphic Design Elements
Read More: What Do Graphic Designers Do? And How To Become One?
Contact US | ThimPress:
Website: https://thimpress.com/
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/ThimPress
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/c/ThimPressDesign
Twitter (X): https://x.com/thimpress_com