Did you know? According to Statista, the global B2B eCommerce market was valued at over $20.4 trillion in 2022, a figure that massively overshadows B2C sales. This statistic isn’t just a number; it’s a testament to the immense power and importance of business-to-business (B2B) transactions in the global economy.
For any entrepreneur, marketer, or small business owner, understanding the B2B model is no longer optional—it’s essential for survival and growth. This guide breaks down exactly what is B2B business, how it fundamentally differs from B2C, and why lasting relationships are more valuable than transaction sizes.
Eduma – Education WordPress Theme
We provide an amazing WordPress theme with fast and responsive designs. Let’s find out!
What is B2B Business? The Core Principles of the B2B Model
At its heart, a Business-to-Business (B2B) company is one that provides products or services directly to other companies and organizations
These transactions form the backbone of nearly every industry. Unlike business-to-consumer (B2C) sales, which are often driven by individual wants and quick decisions, B2B relationships are built on logic, efficiency, and long-term value.
According to Investopedia, these transactions often involve raw materials, enterprise software, manufacturing components, or professional consulting services that enable other businesses to operate, innovate, and grow.

Understanding B2B Transactions
Types of B2B Businesses
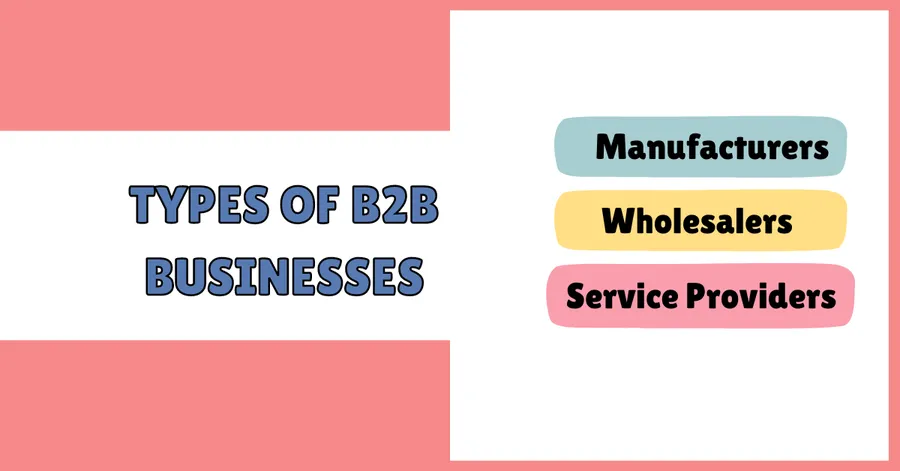
B2B companies encompass various roles within the economic landscape:
- Manufacturers: Companies that produce raw materials or finished goods.
- Wholesalers: Businesses that purchase goods in bulk from manufacturers and resell them to other businesses.
- Service Providers: Organizations that offer specialized services to businesses, such as consulting, marketing, or IT support. For instance, cybersecurity firms providing law firm cybersecurity best practices help protect confidential data and ensure compliance with legal standards.
The B2B Supply Chain

The B2B supply chain involves the movement of raw materials, production, and distribution before reaching the final consumer. This process ensures efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and scalability in business transactions.
Example of a B2B Supply Chain in Action:
- Raw Materials: A textile mill supplies fabric to a clothing manufacturer.
- Production: The manufacturer produces garments and sells them to a wholesaler.
- Wholesale Distribution: The wholesaler supplies clothing to retail stores.
- Retail Sales (B2C): Retail stores sell the clothing to individual consumers.
A well-optimized B2B eCommerce supply chain enhances procurement, logistics, and inventory management, improving business profitability.
Benefits of B2B Transactions
Some benefits of B2B transactions are:
- Increased Efficiency: Specializing allows B2B companies to focus on what they do best.
- Cost Savings: B2B offers volume discounts and streamlined processes.
- Access to Expertise: B2B lets businesses partner with specialists.
Strategies for Reaching B2B Customers
There are some simple but powerful strategies for reaching B2B customers:
- Content Marketing: Create informative blog posts, whitepapers, and webinars.
- Account-Based Marketing (ABM): Develop targeted campaigns for specific high-value accounts.
- Trade Shows and Industry Events: Network and forge connections with potential B2B clients. Tools like Uniqode’s business card can simplify contact sharing, allowing sales representatives to provide direct links to product demos, calendars, or LinkedIn profiles through a quick scan or click.
B2B vs. B2C: Key Differences You Need to Know
While both models involve selling, the approach, audience, and sales process are worlds apart. Understanding these differences is crucial for crafting the right strategy.
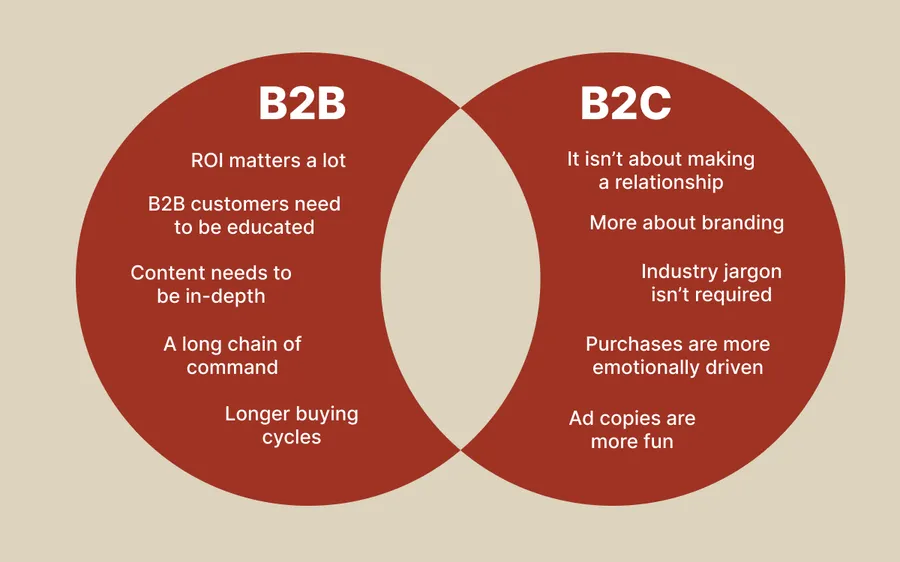
Selling to businesses (B2B) presents a distinct set of challenges compared to selling directly to consumers (B2C).
Here are the fundamental ways B2B sales diverge:
- Complex Decision-Making: B2B purchases often involve longer decision-making cycles. They require approval from multiple stakeholders or even committees, unlike B2C decisions, which are typically made by individuals.
- Formalized Buying Processes: Many businesses have established procurement processes. This means B2B sellers may need to participate in bidding processes or respond to formal Requests for Proposals (RFPs), a practice less common in B2C sales.
- Emphasis on Risk Mitigation: Due to the higher dollar value of B2B transactions, buyers prioritize minimizing risk. They may request product prototypes, customizations, or extensive demonstrations to ensure the solution aligns perfectly with their needs.
- Focus on Logic and ROI: B2B buyers make decisions based on rational factors like cost savings, efficiency gains, and return on investment (ROI). This contrasts with B2C sales, where emotion and personal preferences often play a bigger role.
- Relationship-Driven: Successful B2B salespeople cultivate strong, long-term relationships with key decision-makers within their target companies. Trust and expertise are crucial, as opposed to B2C sales, which often focus on immediate transactions.
B2B and B2C Can Coexist
B2B focuses on transactions between businesses, often involving complex decision-making processes and longer sales cycles.
B2C, on the other hand, emphasizes direct sales to individual consumers, where emotional appeal and quick purchasing decisions are key. They seem worlds apart.
However, the growing complexity of the business landscape means these two models can and do successfully coexist. Here’s how:
- Hybrid Models: Companies can sell to both businesses and individual customers. A software company might offer enterprise-level solutions (B2B) alongside a simpler, consumer-friendly version of its software (B2C).
- Behind-the-scenes B2B: Many consumer products rely on B2B relationships. An online clothing retailer (B2C) needs partnerships with manufacturers, shipping companies, and payment processors (all B2B interactions).
- B2B with a Consumer Focus: Even within traditional B2B, the importance of user experience and strong branding is increasing. B2B buyers are ultimately people too, influenced by elements traditionally seen as B2C-focused.
B2B vs B2C: Simple Comparison Table
| Feature | B2B (Business to Business) | B2C (Business to Consumer) |
|---|---|---|
| Target Audience | Other businesses | Individual consumers |
| Order Size | Large or bulk purchases | Smaller, one-time purchases |
| Decision Process | Slower, involves multiple people | Quick, often emotional decisions |
| Sales Cycle | Longer, relationship-focused | Short, transaction-focused |
| Marketing Approach | Data-driven, ROI-focused | Emotional, brand-driven |
| Examples | Shopify, Alibaba, ThimPress | Amazon, Netflix, Nike |
Building Strong Customer Relationships, Not the Transaction Size
In the world of business to business (B2B), companies sell things to each other. Sometimes these deals are huge, with lots of money changing hands. Other times, a small business might buy a little something from another small business. The most important thing to remember is that it doesn’t matter how much money is involved – every customer is valuable.
Reasons to focus on the customer matters:
- Repeat Business: Happy customers, whether they buy a little or a lot, are likely to come back for more. This builds strong business relationships.
- Word of Mouth: Satisfied companies will talk! They tell their business friends, which could lead to even more customers for you.
- Growth: Every customer contributes to your business’s growth. Smaller deals can eventually lead to larger opportunities.
Here are how to put the customer first:
- Excellent Customer Service: Treat every customer like they’re your most important one. Be helpful, and quick to solve problems.
- Build Relationships: Get to know your customers’ needs. This way, you can offer them exactly what will help their businesses succeed.
- Personalized Touch: Even small transactions deserve a touch of personalization. This makes customers feel valued.
Focusing on building great customer relationships, not just on how big a sale is, is the key to long-term success in B2B. A loyal customer base is worth its weight in gold!
Common Types of B2B Companies
B2B is not a monolith. It encompasses a wide range of companies that fit into three main categories:
- Manufacturers: These companies produce physical goods, from raw materials like steel to finished components like microchips, which are then sold to other businesses.
- Wholesalers & Distributors: They act as intermediaries, purchasing goods in bulk from manufacturers and reselling them to retailers or other businesses.
- Service Providers: This is a vast and growing category. It includes companies offering specialized services like:
- SaaS (Software-as-a-Service): Think Slack, Salesforce, or Adobe.
- Professional Services: Law firms, accounting agencies, marketing consultants.
- IT & Tech Support: Companies that manage another business’s technology infrastructure.
Essential B2B Marketing & Sales Strategies
Reaching business customers requires a targeted, value-driven approach. Here are some of the most effective strategies:
Content Marketing
Create high-value, informative content that solves your target audience’s problems. This includes detailed blog posts, in-depth whitepapers, case studies, and educational webinars that establish your company as a thought leader.
Account-Based Marketing (ABM)
Instead of casting a wide net, ABM focuses marketing and sales resources on a specific set of high-value target accounts. It’s a highly personalized approach that treats each company as its own market.
Industry Networking & Trade Shows
In B2B, personal connections matter. Attending trade shows and industry events is a powerful way to build relationships, generate leads, and understand market trends. Digital tools like QR code business cards can streamline contact sharing and follow-ups.
Real-World Examples of B2B Businesses
ThimPress – LearnPress & Eduma Themes
What it does:
ThimPress develops WordPress themes and plugins like LearnPress (a learning management system) and Eduma, a popular education theme.
Why it’s B2B:
These tools are designed for businesses such as schools, online course creators, and education providers to build their platforms and sell courses — making it a classic B2B service.
Shopify: Powering Online Stores
What it does:
Shopify provides tools and technology that help other businesses create and manage online stores. While consumers use the stores built with Shopify, the platform itself is B2B — it’s built for businesses.
Why it’s B2B:
Shopify doesn’t sell to customers directly. Instead, it gives business owners the tools they need to sell to consumers (B2C).
Alibaba: Wholesale Marketplace
What it does:
Alibaba connects manufacturers and suppliers with retailers and wholesalers around the world.
Why it’s B2B:
The platform facilitates bulk orders, helping businesses source products at low prices and resell them. Consumers don’t typically shop on Alibaba — other businesses do.
Slack: Team Communication Software
What it does:
Slack provides communication tools that help teams collaborate better — especially remote teams.
Why it’s B2B:
Slack sells its services directly to companies and organizations, not to individuals, making it a perfect example of B2B SaaS (Software as a Service).
How to Measure Success: Key B2B Metrics (KPIs)
To grow a B2B company, you need to track the right metrics. The focus is on long-term value, not just single transactions.
- Customer Lifetime Value (CLV): The total revenue a business can expect from a single customer account throughout the relationship.
- Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC): The total cost of sales and marketing to acquire a new customer. A healthy business model requires CLVCAC.
- Return on Investment (ROI): The profit generated from marketing and sales investments. In B2B, this is often calculated for specific campaigns or channels to determine what works best.
Conclusion: What Is B2B Business?
Understanding B2B ecommerce provides a crucial advantage in the business world. By mastering the complexities, building strong relationships, and offering compelling solutions, your business can thrive in this dynamic landscape.
FAQs about B2B:
Clients often place repeat orders.
Sales tend to be high in value.
Relationships can last for years, leading to stable revenue.
In fact, the B2B market is larger than B2C — global B2B ecommerce was worth $20.4 trillion in 2022, which is 5 times bigger than B2C ecommerce.
Examples:
A freelance graphic designer offering branding services to startups.
A local printer providing packaging for small online sellers.
A web developer creating websites for local businesses.
Small-scale B2B operations can still bring in steady income and long-term clients.
Read More:
How To Create Menu In Eduma Theme: A Step-by-Step Guide