FOMO marketing (Fear of Missing Out marketing) is a powerful psychological strategy used to accelerate consumer decisions and enhance sales.
It taps into the fundamental human anxiety of being excluded from a rewarding experience, a valuable opportunity, or a popular trend. By skillfully creating a sense of urgency and scarcity, brands can significantly reduce hesitation and encourage immediate action.
This comprehensive guide will explore the depths of FOMO marketing, moving from its psychological origins to practical, actionable strategies.
We will analyze why this technique is so effective in the digital age and provide numerous FOMO marketing examples to illustrate how you can implement these concepts ethically and successfully.
Whether you are in eCommerce, software, or retail, understanding FOMO in marketing is essential for staying competitive.
Eduma – Education WordPress Theme
We provide an amazing WordPress theme with fast and responsive designs. Let’s find out!
What is FOMO?

FOMO, an acronym for “Fear of Missing Out,” is a distinct form of social anxiety. It is characterized by the desire to remain continually connected with what others are doing. A study published in Computers in Human Behavior defines it as “a pervasive apprehension that others might be having rewarding experiences from which one is absent.”
This feeling is not new, but it has been significantly amplified by social media. Platforms like Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok present curated, continuous streams of highlights from other people’s lives—travel, achievements, social gatherings, and purchases.
This constant exposure can trigger a persistent feeling that one’s own life is less exciting or that they are missing out on important social events or trends. This psychological phenomenon drives individuals to seek information, engage in social connections, and make decisions primarily to avoid the negative feeling of exclusion.
What is FOMO Marketing?

FOMO marketing is the strategic application of this psychological trigger to influence consumer behavior. It involves creating marketing messages and campaigns that imply an offer is limited, exclusive, or in high demand, thereby compelling the audience to act quickly to avoid the “pain” of missing out.
By generating a sense of exclusivity, scarcity, and time-sensitive opportunities, FOMO marketing taps directly into the emotional response triggered by potential loss.
This technique is highly effective because it bypasses prolonged deliberation. It captures attention, creates a powerful sense of urgency, and motivates consumers to convert—whether that means making a purchase, subscribing to a newsletter, or signing up for an event.
A well-executed FOMO marketing strategy makes the customer feel they are seizing a valuable opportunity that might not be available later.
Why is FOMO in Marketing So Effective?
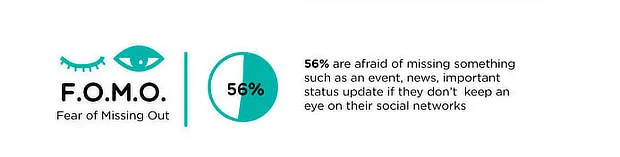
The effectiveness of FOMO in marketing is not just anecdotal; it is supported by significant psychological principles and consumer data.
First, consider the data. Research indicates that FOMO is most prevalent among millennial and Gen Z consumers.
According to data reported by Strategy Online, approximately 69% of millennials experience this phenomenon, and a remarkable 60% make impulsive, reactive purchases because of it.
They buy something not just because they want it, but because they fear the regret of not buying it. With billions of active social media users worldwide, this creates a vast audience already primed for such messaging.
Second, FOMO marketing leverages two core principles of behavioral psychology:
- Loss Aversion: Popularized by psychologists Daniel Kahneman and Amos Tversky, this principle states that the psychological pain of losing something is roughly twice as powerful as the pleasure of gaining something equivalent. FOMO tactics frame a non-purchase as a loss—losing a discount, losing access, or losing a product.
- Social Proof: This concept, detailed by Robert Cialdini, describes our tendency to rely on the actions of others to determine our own behavior, especially in situations of uncertainty. When we see that a product is “best-selling” or that “1,200 people signed up today,” it validates the decision and creates a fear of being the only one not participating.
In short, FOMO marketing works because it aligns perfectly with fundamental human cognitive biases. It shifts the consumer’s mindset from “Do I need this?” to “Will I regret not getting this?”
A Successful FOMO Marketing Strategy

A successful FOMO marketing strategy is not just about randomly applying tactics. It is built upon four interconnected pillars that work together to create a compelling incentive for the customer.
Urgency
Urgency compels customers to act now rather than later. Procrastination is the enemy of conversion, and urgency is its direct antidote. This pillar relies on time-sensitivity.
- Tactics: Limited-time offers (“Sale ends at midnight”), flash sales (“Today only”), and holiday promotions.
- Visual Tools: The most effective tool for urgency is a countdown timer. Displaying a live clock ticking down on a product page or in an email visually reinforces the disappearing nature of the offer, creating tangible pressure to act.
Scarcity
Scarcity increases the perceived value of a product or service by highlighting its limited availability. If something is difficult to obtain, it is psychologically perceived as being more valuable.
- Tactics: Displaying low stock levels (“Only 3 left in stock!”), limiting purchase quantities (“Limit 2 per customer”), or creating limited-edition product drops.
- Example: The “sneaker drop” model used by brands like Nike is a masterclass in scarcity. By releasing a limited number of shoes at a specific time, they create a massive surge in demand and sell out in minutes.
Exclusivity
Exclusivity makes the customer feel special, as if they are part of a select “in-group” receiving special treatment. This taps into the human desire to belong and to have a higher status.
- Tactics: VIP memberships, “early access” for email subscribers, member-only sales, or access to private communities.
- Example: Amazon Prime Day is a global FOMO marketing event built entirely on exclusivity. The deals are only available to Prime members, encouraging millions to sign up to avoid missing out.
Social Proof
Social Proof validates a customer’s decision by showing that others have already made the same choice. It answers the subconscious question, “Am I making a mistake?” with a resounding “No, everyone is doing it.”
- Tactics: Displaying customer testimonials and reviews, showcasing user-generated content (UGC), showing live activity feeds (“Someone in New York just bought…”), and highlighting popularity (“Best-Seller” or “Trending”).
- Example: Booking.com famously uses social proof by stating, “Booked 5 times in the last 24 hours,” right on the hotel listing.
17 Powerful FOMO Marketing Examples in Action
Let’s move from theory to practice. Here are 17 FOMO marketing examples that demonstrate how these strategies are used by real brands to drive conversions.
Examples of Urgency
- Countdown Timers: Amazon’s “Deal of the Day” is a classic example. A prominent countdown timer ticks down the hours, minutes, and seconds until the deal expires. This visual representation of vanishing time creates immense pressure to purchase immediately.
- Flash Sale Announcements: Announcing a surprise sale that lasts only a few hours (“Flash Sale: 40% Off for 3 Hours!”) is a powerful tactic. This works exceptionally well on social media and in email newsletters, rewarding followers who act quickly.
- Expiring Content: Snapchat built its entire platform on this concept. In a business context, this can be a B2B webinar that is “only available live” or a company announcing it is “locking in old pricing” for 24 hours before a price increase.
- Limited-Time Shipping Offers: How many times have you added an item to your cart to get “Free shipping on orders over $50”? Brands also use urgency by offering “Free shipping ends tonight!” This can be the final nudge a customer needs to complete their purchase.
Examples of Scarcity
- Displaying Stock Levels: Amazon excels at this with its “Only 3 left in stock – order soon” messaging. This simple line communicates high demand and scarcity, forcing the customer to decide before someone else gets the last one.
- Highlighting Missed Opportunities: Travel site Booking.com is a master of this. By showing “You missed it! Our last room at this price was just booked” in big red letters, it trains users to act faster on the next listing they see.
- Showing Limited Availability: This is another Booking.com specialty. Messages like “Only 2 rooms left at this price” or “In high demand!” create a competitive environment where the user feels they must book now or lose the opportunity.
- Limited-Edition Products: From sneaker “drops” by Nike to limited-edition flavors by food companies, this strategy makes a product an instant collectible. The scarcity is genuine, and the FOMO it generates is immense.
Examples of Social Proof
- Live Sales Notifications: Small popups that state “Sarah in New York just purchased a 3-Month Plan” create a dynamic sense of a busy, trusted store. It tells new visitors that real people are buying products right now.
- Displaying Best-Sellers: Highlighting a “Best-Sellers” or “Most Popular” category, as cosmetics company ColorPop does, acts as a massive “in-group” signal. New visitors are guided to products that are already validated by thousands of other customers.
- Showing Viewer/Buyer Counts: This tactic combines social proof with competition. Booking.com’s “5 people are looking at this property right now” implies you need to act fast. Amazon’s “100+ bought in the past month” confirms a product’s popularity.
- User-Generated Content (UGC): When Wayfair encourages users to post photos with the #wayfairathome hashtag, it showcases real people enjoying its products in real homes. This authentic social proof is far more compelling than any professional ad.
- Reviews and Ratings: The simple presence of a 5-star rating next to a product is a form of passive social proof. It reassures visitors that past purchasers were satisfied, reducing friction in the buying process.
Examples of Exclusivity
- VIP & Early Access: Amazon Prime Day is one of the largest FOMO marketing examples on Earth. It’s a global sales event where the best deals are only available to Prime members. This exclusivity drives millions of signups and sales.
- Rewarding Early Decisions: Offering a special gift or discount to the “first 100 customers” creates a rush at launch. This rewards your most loyal fans and leverages their enthusiasm to build buzz.
- Gated Content: Offering a high-value whitepaper, e-book, or webinar “exclusively” for email subscribers makes that content feel more valuable. The content is “locked,” and the only way to get in is to join the exclusive group.
- Explicit “Don’t Miss Out” Messaging: Sometimes, the most direct approach works best. Brands like Rue La La use copy like “Don’t Miss Out” paired with images of an exclusive, high-end party. The message is clear: join us, or be left out of the fun.
Building Effective FOMO Marketing Campaigns
Knowing the examples is one thing; implementing them is another. Here is how to build effective FOMO marketing campaigns that are both powerful and responsible.
Know Your Audience
As the FOMO marketing research shows, some demographics (like millennials) are more susceptible to FOMO. Understand who your customer is and what motivates them. A 20-year-old might respond to social proof on TikTok, while a 45-year-old might respond better to an email offering “early access” and exclusive status.
Use Authentic Triggers
This is the most important rule. Your urgency and scarcity must be real. If you say “Only 2 left!” but if you have a warehouse full, customers will eventually find out. If your “24-Hour Sale” runs all week, you destroy all trust. E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness) is paramount in SEO, and trust is your most valuable asset.
Leverage the Right Channels
- Email Marketing: This is perfect for FOMO marketing campaigns. Use it for cart abandonment emails (“Your items are selling out!”), last-chance reminders for sales, and delivering exclusive subscriber-only deals.
- Website Popups: Use exit-intent popups to present a final, time-sensitive offer to a visitor who is about to leave. “Wait! Get 10% off for the next 15 minutes.”
- Social Media: This channel is ideal for flash sales, influencer takeovers (exclusivity), and promoting your user-generated content (social proof).
A/B Test Your Messaging
Do not assume what works. Test your FOMO marketing tactics. Does “Only 3 left” convert better than “Selling fast”? Does a red countdown timer work better than a black one? Use A/B testing to find the most effective language and design for your specific audience.
The Ethics of FOMO Marketing
It is essential to address the ethical considerations of FOMO marketing. Because it leverages anxiety, it can be perceived as manipulative. The line between persuasion and manipulation is thin.
To use FOMO marketing ethically, follow these best practices:
- Be Honest: As stated above, never lie about stock levels or time limits. Fake scarcity is deceptive and will damage your brand reputation.
- Provide Genuine Value: FOMO should be used to highlight genuine value, not invent it. The underlying offer—the product, the discount, the content—must be good. FOMO should just accelerate the decision to accept that value.
- Avoid Creating Panic: The goal is to create excitement and urgency, not debilitating anxiety. Avoid using high-pressure tactics on essential services or vulnerable populations.
When used responsibly, FOMO marketing is a positive force. It helps customers discover good deals and make decisions, while simultaneously helping businesses drive conversions.
Conclusion: Making FOMO Work for You
FOMO marketing is one of the most powerful tools in the modern marketer’s toolkit. It is not a gimmick but a strategy grounded in fundamental human psychology: our fear of loss, our need for social validation, and our desire to belong.
By understanding its core components—urgency, scarcity, social proof, and exclusivity—you can move beyond simple sales pitches and create compelling experiences that resonate with customers.
When used ethically and authentically, FOMO in marketing benefits everyone. It cuts through the noise, helps customers make confident decisions, and drives tangible growth for your business.
Start small. Pick one FOMO marketing strategy from this guide. Add stock levels to your product pages, feature your best-selling items more prominently, or run a one-day flash sale for your email subscribers. By respectfully tapping into the fear of missing out, you can create a new level of engagement and loyalty.
FAQs about FOMO Marketing
1. What is FOMO in marketing?
FOMO, or “Fear of Missing Out,” in marketing is a strategy that uses psychological triggers to create anxiety in consumers that they might miss out on a product, experience, or offer. This encourages them to make a faster purchasing decision.
2. How do you create FOMO in marketing? You can create FOMO by implementing four main tactics:
You can create FOMO by implementing four main tactics:
Urgency: (e.g., “Limited-time offer,” countdown timers)
Scarcity: (e.g., “Only 5 left in stock”)
Social Proof: (e.g., “1,000 people bought this,” user reviews)
Exclusivity: (e.g., “Members-only access,” “VIP sale”)
3. Is FOMO marketing ethical?
FOMO marketing is ethical when it is truthful and highlights genuine value. It becomes unethical if it relies on deception, such as fake scarcity (lying about stock levels) or false urgency (a “limited-time” sale that never ends), to manipulate consumers.
4. What are some common FOMO marketing examples?
Common FOMO marketing examples include Amazon’s “Deal of the Day” countdown timers, Booking.com’s “Only 2 rooms left” notifications, live sales popups (“Someone just bought…”), and exclusive “early access” sales for email subscribers.
5. What does FOMO stand for in business?
In business, FOMO stands for “Fear of Missing Out.” It refers to the strategy of leveraging this consumer fear to accelerate purchasing decisions, increase conversion rates, and drive sales.
6. What are FOMO ads?
FOMO ads are advertisements specifically designed to create a sense of urgency or scarcity. They often use language like “Flash Sale Ends Tonight!,” “Limited Edition,” or “Don’t Miss Out” to encourage an immediate click and conversion from the viewer.
Read more: A Guide to The 14 Best Email Marketing Platforms
Contact US | ThimPress:
Website: https://thimpress.com/
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/ThimPress
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/c/ThimPressDesign
Twitter (X): https://x.com/thimpress_com



