Online security is critical in the modern digital world. Whether you’re browsing the web, shopping online, or sharing personal information, ensuring your data is protected is crucial.
One technology that plays a significant role in safeguarding online interactions is the SSL certificate. But what exactly is it, and why is it so important?
In this beginner’s guide, we’ll delve into the world of SSL certificates, exploring their purpose, functionality, and benefits.
Eduma – Education WordPress Theme
We provide an amazing WordPress theme with fast and responsive designs. Let’s find out!
What is SSL?
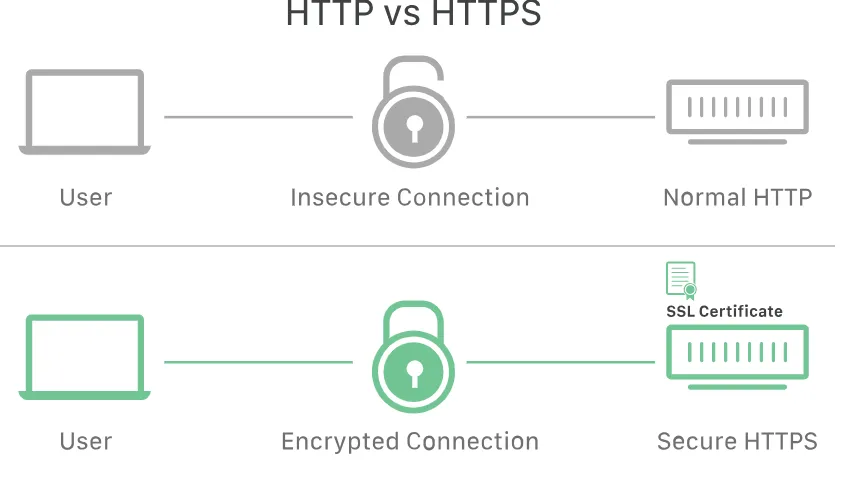
SSL, short for Secure Sockets Layer, is a cryptographic protocol designed to secure communications over a computer network.
Developed by Netscape in 1995, its primary purpose was to establish privacy, authentication, and data integrity for Internet communications. SSL is the foundation upon which the modern Transport Layer Security (TLS) protocol is built.
In essence, SSL/TLS acts as a protective layer between your web browser and the website server you’re interacting with. It encrypts the data transmitted between the two, ensuring that sensitive information like passwords, credit card numbers, and personal details remain confidential and secure from prying eyes.
One of the easiest ways to identify a website that has implemented SSL/TLS is to look for “HTTPS” in the URL instead of “HTTP.” The “S” stands for secure, signifying the presence of the SSL/TLS protocol and the encryption it provides.
What is an SSL certificate?
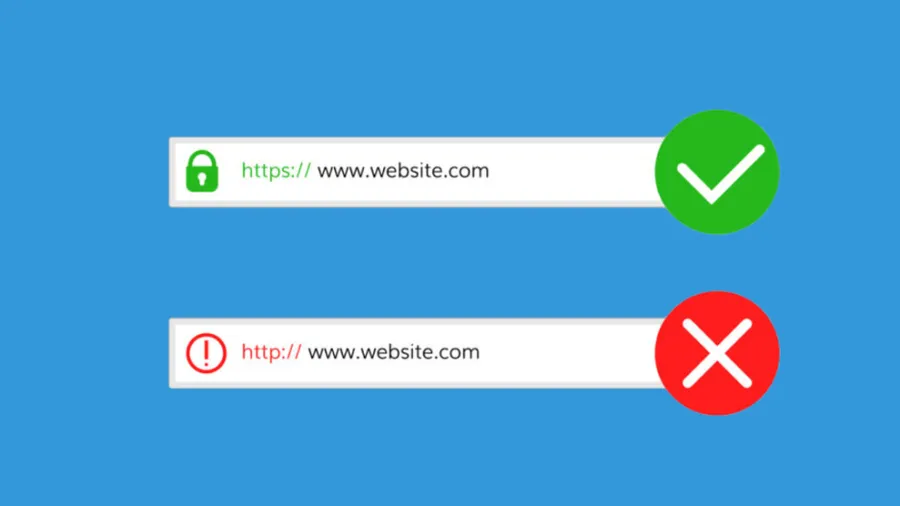
An SSL certificate is a digital certificate that authenticates a website’s identity and allows for a secure, encrypted connection between a web server and a web browser.
This encryption protects sensitive information transferred between the two systems, ensuring it cannot be intercepted or modified by malicious actors.
When a website is secured with an SSL certificate, you’ll typically see a padlock icon next to the URL in your address bar. While the technology has evolved from SSL to TLS, the term SSL is still commonly used to refer to this type of digital certificate.
How do SSL certificates work?
SSL certificates are digital files that establish a secure, encrypted connection between a web server and a user’s browser. This ensures that sensitive information, like passwords and credit card numbers, is transmitted safely.
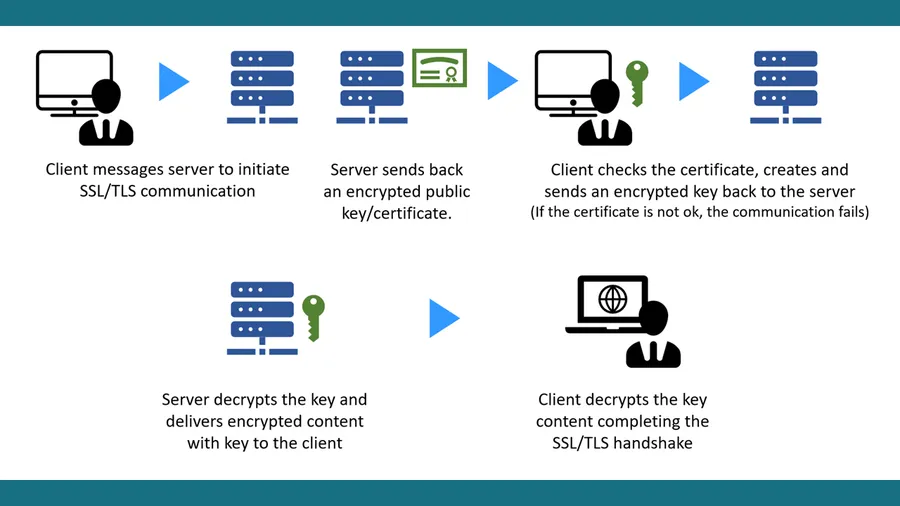
Here’s a simplified explanation of how they work:
- Certificate Information: SSL certificates contain crucial details such as the domain name, owner, issuer (Certificate Authority), public key, and validity dates. The public key is used to encrypt data, while the corresponding private key (kept secret on the server) decrypts it.
- Establishing the Connection: When you visit a website with HTTPS, your browser requests the SSL certificate from the server.
- Verification: Your browser verifies the certificate’s authenticity by checking if it’s issued by a trusted Certificate Authority and if the domain name matches. If it passes the checks, the connection is deemed secure.
- Encryption: The browser and server generate unique session keys using the public and private keys. These session keys encrypt all data exchanged during your visit, ensuring confidentiality and integrity.
- Decryption: The server uses its private key to decrypt the data, allowing it to understand and process your requests.
Why you need an SSL certificate
Websites need SSL certificates for the following reasons:
- Data Encryption: SSL certificates enable encryption of data transmitted between the website and its users, protecting sensitive information like login credentials and credit card details from interception by hackers.
- Authentication: SSL certificates verify the website’s identity, assuring users that they are interacting with a legitimate site and not a malicious imposter.
- Trust and Credibility: The presence of an SSL certificate, indicated by the padlock icon and “https://” in the address bar, enhances user trust and confidence in the website’s security and legitimacy.
- SEO Benefits: Search engines like Google prioritize websites with SSL certificates, giving them a slight ranking advantage in search results.
Types of SSL certificates

SSL certificates secure websites and online transactions by encrypting data and verifying the identity of website owners.
They come in various types with different levels of validation and functionality:
- Extended Validation (EV SSL): The most rigorous validation process. Websites using EV SSL display a green address bar and the organization’s name, instilling the highest trust among users.
- Organization Validated (OV SSL): Verifies the identity of the organization behind the website, providing a moderate level of trust.
- Domain Validated (DV SSL): The most basic validation level, confirming only domain ownership. While it encrypts data, it doesn’t offer the same visual trust indicators as EV or OV SSL.
- Wildcard SSL: Secures a primary domain and all its subdomains with a single certificate. This is cost-effective for websites with multiple subdomains.
- Multi-Domain SSL (MDC): Secures multiple distinct domains with a single certificate, ideal for organizations managing several websites.
- Unified Communications Certificate (UCC): Specifically designed for Microsoft Exchange and Office Communications servers, securing various communications services.
How to obtain an SSL certificate
Websites obtain SSL certificates through a process that involves Certificate Authorities (CAs). These trusted third-party organizations verify the website’s identity and issue a digital certificate. Here’s a simplified breakdown:
- Preparation: The website owner ensures their server is set up correctly and their WHOIS record is accurate.
- CSR Generation: A Certificate Signing Request (CSR) is generated on the server, often with help from the hosting provider.
- Submission: The CSR is submitted to a CA, which validates the domain and company details.
- Validation: The CA performs different levels of validation depending on the certificate type, ranging from quick domain validation to extended validation that takes longer.
- Issuance and Installation: Once validated, the CA issues the SSL certificate, which is then installed on the web host or server.
The cost and time to obtain an SSL certificate vary depending on the level of validation and the chosen CA. Some providers offer free options, while others charge fees based on the desired security level.
Is it possible to get a free SSL certificate?

Yes, you can get a free SSL certificate. Cloudflare or Let’s Encrypt is a popular provider that pioneered this option, offering free shared SSL certificates for most websites. To obtain one, simply sign up for an account, add your website, and enable SSL in the settings.
Other providers offer free SSL certificates, so it’s worth exploring your options to find the best fit for your needs.
Can an SSL certificate be used on multiple servers?
Yes, an SSL certificate can be used on multiple servers. This is often done for load balancing or to secure multiple subdomains with a wildcard certificate. However, it requires careful management of the private key and may have licensing restrictions depending on the certificate authority.
Conclusion
SSL certificates are a fundamental pillar of online security, protecting sensitive data and building trust with your audience. Understanding their role and importance empowers you to make informed decisions about securing your website and online activities.
Read More: 8+ Top Google Domains Alternatives (Compared)
Contact US | ThimPress:
Website: https://thimpress.com/
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/ThimPress
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/c/ThimPressDesign
Twitter (X): https://x.com/thimpress_com



