The 7Ps of Marketing is an expanded version of the traditional marketing mix, designed to help businesses plan, execute, and optimize their marketing strategy in both product- and service-based markets.
While the original 4Ps (Product, Price, Place, Promotion) focus mainly on tangible products, the 7 Ps marketing mix adds People, Process, and Physical Evidence, making it far more relevant in today’s service-driven and digital-first economy.
If you’re wondering what are the 7Ps of marketing, how they work, and how to apply them in real business situations, this guide will walk you through everything step by step.
What is A Marketing Mix?
The marketing mix refers to a combination of controllable variables that a company uses to influence customer buying decisions. These variables help marketers position products or services in a way that meets customer needs while achieving business objectives.
Initially, the marketing mix consisted of the 4Ps:
- Product
- Price
- Place
- Promotion
As markets evolved and services became more dominant, the model expanded into the 7Ps of marketing, also known as the extended marketing mix.
What Are the 7Ps of Marketing?
The 7Ps of Marketing include:
- Product
- Price
- Place
- Promotion
- People
- Process
- Physical Evidence
Together, these elements create a practical framework that helps businesses:
- Understand customer needs
- Design competitive offerings
- Deliver consistent brand experiences
- Optimize marketing performance
Who Developed The 7Ps of Marketing?
E. Jerome McCarthy was the original developer of the 7Ps of marketing, and he introduced them in 1960 in his book Basic Marketing. A Managerial Approach.

The 7Ps of Marketing Explained (In Detail)
1. Product
Product refers to what you offer to meet customer needs—whether it’s a physical product, a digital product, or a service.
Key considerations:
- Features and functionality
- Quality and reliability
- Design and packaging
- Product lifecycle
- Unique value proposition
Example:
A SaaS platform focuses on ease of use, integrations, and customer support rather than physical attributes.
Product checklist:
- Does the product solve a real customer problem?
- What makes it better than competitors?
- Is it aligned with your brand positioning?
2. Price
Price is the amount customers are willing to pay in exchange for the value your product or service provides.
Pricing directly affects:
- Brand perception
- Profit margins
- Market competitiveness
Common pricing strategies:
- Penetration pricing
- Premium pricing
- Competitive pricing
- Freemium or subscription-based pricing
Price checklist:
- Is your pricing aligned with perceived value?
- Can your target audience afford it?
- How does your price compare to competitors?
3. Place
Place refers to where and how customers access your product or service.
This includes:
- Physical stores
- E-commerce websites
- Marketplaces
- Distribution partners
Example:
An online course platform delivers content globally through a website, eliminating the need for physical locations.
Place checklist:
- Where do your customers expect to find you?
- Are your distribution channels convenient?
- Is your product accessible on mobile devices?
4. Promotion
Promotion covers all communication activities used to inform, persuade, and remind customers about your offering.
Promotion channels include:
- Content marketing
- Social media marketing
- Search engine marketing (SEO & PPC)
- Email marketing
- Public relations
Promotion checklist:
- Are you promoting on the channels your audience uses?
- Is your messaging consistent across platforms?
- Are you measuring campaign performance?
5. People
People include everyone involved in delivering your product or service—from sales teams to customer support.
Strong people strategies improve:
- Customer satisfaction
- Brand loyalty
- Service quality
People checklist:
- Are employees trained and motivated?
- Do they represent your brand values?
- Is customer feedback taken seriously?
6. Process
Process refers to the systems and workflows that deliver value to customers.
This includes:
- Ordering and payment systems
- Customer onboarding
- Service delivery
- Complaint handling
Process checklist:
- Are your processes efficient and user-friendly?
- Are there friction points in the customer journey?
- Can processes scale with growth?
7. Physical Evidence
Physical Evidence is what customers see and experience when interacting with your brand.
Examples include:
- Website design
- Branding and logos
- Packaging
- Reviews and testimonials
- Receipts and confirmation emails
Physical evidence checklist:
- Does your brand look trustworthy?
- Is your online presence professional?
- Do customers receive tangible proof of value?
What is Different Between The 4Ps vs 7Ps of Marketing?
| 4Ps | 7Ps |
|---|---|
| Product | Product |
| Price | Price |
| Place | Place |
| Promotion | Promotion |
| — | People |
| — | Process |
| — | Physical Evidence |
The 4Ps of marketing were created at a time when businesses were more likely to sell products than services. 4Ps were focused on only product marketing, and people did not know how important customer service was for building a brand.
Booms and Pitner later added three additional ‘service mix P’s’: Participants or People, Physical evidence, and Processes. They also changed from ‘Participants’ to ‘People’, referring to the model marketing mix that includes marketers, remuneration, customer service representatives, culture, recruitment, and training.
When examining competitive strategies nowadays, the complete 7Ps of marketing need to be taken into consideration.
The 7Ps assist businesses in evaluating and defining the main issues affecting the marketing of their products and services. The marketing mix, a well-known marketing model, is also understood as the 7Ps model for the digital marketing mix.
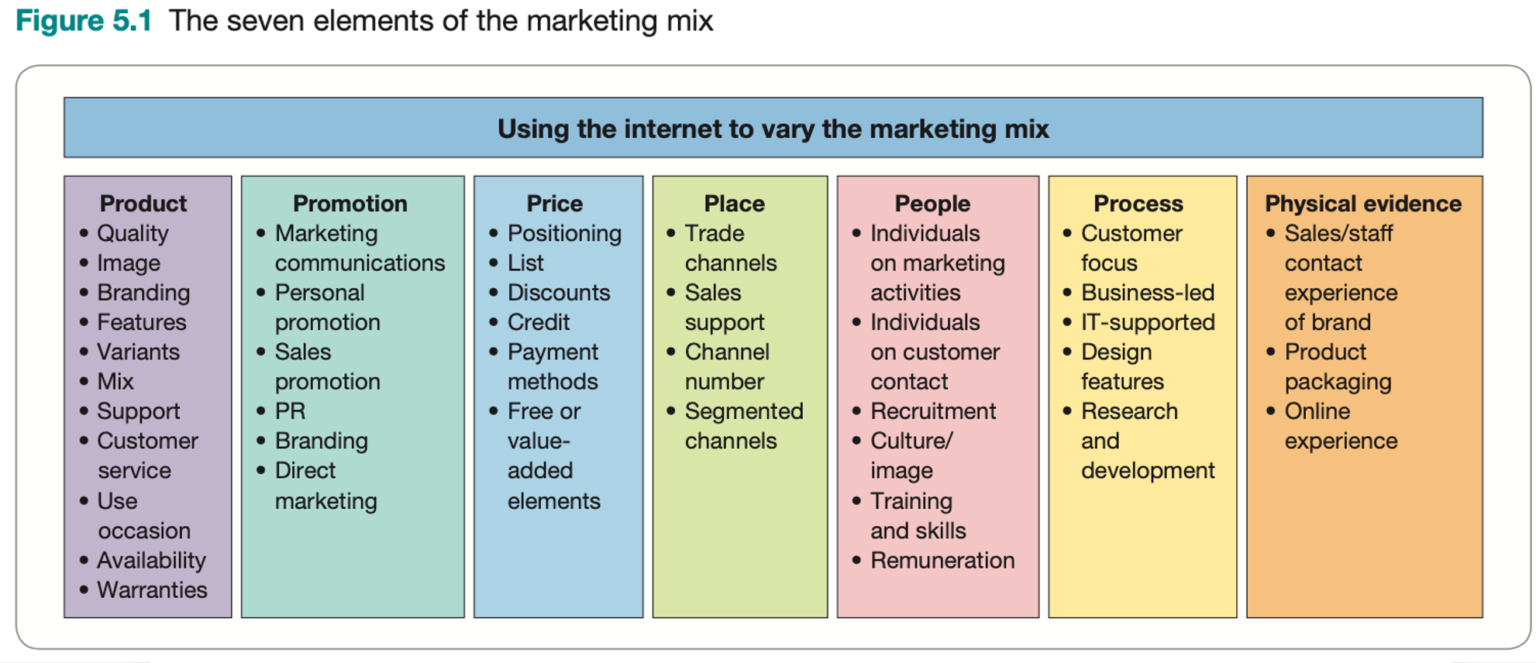
This model was updated and applied to online channels in Dave Chaffey‘s book, Digital Marketing: Strategy, Implementation, and Practice, to provide a realistic approach that fits different business channels.
Some suggest adding an eighth P, ‘Partners’, for businesses to increase their online reach (first mentioned in Digital Marketing Excellence by Dave Chaffey and PR Smith, even though others would claim it’s part of Place).
How to Use The 7Ps of Marketing
We think the 4Ps are a vital strategic tool to choose their scope and are especially helpful for small businesses, even though some may consider them outdated.
The 7Ps of Marketing can also assist companies in setting objectives, executing a SWOT analysis, and undertaking competitive analysis. It’s a pragmatic framework to review an existing business and employ appropriate methods while evaluating the elements of the marketing mix.
Real Examples of the 7Ps of Marketing
Example: A Digital Marketing Agency
- Product: SEO and content marketing services
- Price: Monthly retainer packages
- Place: Online delivery via website and email
- Promotion: Blog content, social media, webinars
- People: Strategists, account managers, content writers
- Process: Onboarding → strategy → execution → reporting
- Physical Evidence: Case studies, reports, client testimonials
This integrated approach ensures consistency across all marketing touchpoints.
Pros and Limitations of the 7Ps Model
Advantages:
- Comprehensive and flexible
- Customer-focused
- Works well for services and digital businesses
Limitations:
- Can be complex for small teams
- Requires constant optimization
- Doesn’t fully address branding or innovation
FAQs About the 7Ps of Marketing
What are the 7Ps of marketing?
They are Product, Price, Place, Promotion, People, Process, and Physical Evidence.
Why are the 7Ps important?
They help businesses create balanced, customer-focused marketing strategies.
What is the difference between 4Ps vs 7Ps?
The 7Ps expand the original 4Ps by including service-related elements.
Are the 7Ps still relevant in digital marketing?
Yes. They are highly adaptable to digital and service-based models.
Conclusion
The 7Ps of Marketing provide a practical framework for building effective, customer-centric marketing strategies. By understanding and optimizing each element of the marketing mix, businesses can improve customer experience, strengthen brand positioning, and achieve sustainable growth.
When applied correctly, the 7 Ps marketing mix helps ensure that every aspect of your marketing works together toward a unified goal.
Read More: What is the AIDA model in marketing?
Contact US | ThimPress:
Website: https://thimpress.com/
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/ThimPress
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/c/ThimPressDesign
Twitter (X): https://x.com/thimpress_com



