Are you finding it difficult to drive organic traffic to your online store using only product descriptions? While Adobe Commerce (formerly Magento) is a powerhouse for sales, it often lacks the intuitive content management capabilities needed to build a loyal audience.
Combining your eCommerce engine with a dedicated Content Management System (CMS) is the solution. This guide provides a comprehensive Magento WordPress integration tutorial, designed to help you merge the blogging power of WordPress with the scalability of Magento.
Claue – Clean and Minimal Magento Theme
We provide an amazing Magento theme with fast and responsive designs. Let’s find out!
What is Magento WordPress Integration?
Magento WordPress integration is the technical process of connecting the Magento eCommerce platform with the WordPress CMS. This unification allows store owners to manage complex product catalogs and transactions via Magento while utilizing WordPress to create engaging blog posts, landing pages, and media content.
The result is a hybrid website where the shopping cart and the blog share the same theme, header, footer, and user session, appearing as a single, cohesive site to the visitor.
Why Connect Magento and WordPress?
There are several strategic reasons to integrate Magento with WordPress. Doing so leverages the specific strengths of both platforms without compromising on performance.
- Unified User Experience (UX): Customers can move seamlessly from reading a blog post to adding a product to their cart without noticing they have switched platforms.
- Superior SEO Capabilities: WordPress offers advanced SEO plugins and content structures that are often easier to manage than Magento’s native CMS features, helping you rank higher for informational keywords.
- Shared Branding: Integration ensures your fonts, colors, and layout remain consistent across the entire site, building trust and professional credibility.
- Single Sign-On (SSO): A deeper integration allows customers to log in once and access their account details on both the blog and the store.
- Cart Accessibility: You can display the Magento shopping cart status (e.g., “2 items in cart”) directly on the WordPress interface.
Magento WordPress Integration Methods
There are two primary ways to approach this setup. The method you choose depends on your existing infrastructure and business goals.
- WordPress on Magento: Best for existing eCommerce stores that want to add a blog. The blog lives inside the Magento file structure.
- Magento on WordPress: Best for content-heavy sites that want to add simple eCommerce functionality. Magento operates as a backend service for the WordPress frontend.
Method 1 (Installing WordPress on Magento)
This is the most common approach for eCommerce-first businesses. It involves placing WordPress files within your Magento directory and using an extension to bridge the gap.
Step 1: Install WordPress Files
To begin, you must manually set up the WordPress core files on your server.
- Navigate to the official WordPress website and download the latest version.
- Access your Magento root directory via your file manager or FTP.
- Upload and extract the WordPress files here.
- Important: Rename the extracted folder to something simple like wp to keep your file structure clean. Avoid naming it blog if you want your URL to be site.com/blog, as this can cause routing conflicts later.
- Open your browser and navigate to your domain.com/wp. Follow the standard WordPress on-screen installation prompts to set up the database and admin user.
Step 2: Install the Integration Module
To fully connect Magento and WordPress, you need an extension that allows them to talk to each other. The FishPig extension is a widely accepted industry standard for this.
- Download the integration extension (e.g., FishPig).
- Upload the extension files to the app/code/ directory in your Magento installation.
- Open your server terminal (SSH) and run the module enablement command: php bin/magento module:enable FishPig_WordPress
Step 3: Configure the Settings
Once installed, you must link the two platforms via the Magento Admin Panel.
- Log in to Magento and navigate to WordPress > Settings.
- Database Integration: Configure how the databases communicate (most extensions handle this automatically if on the same server).
- Path Settings: Enter the local file path where you installed WordPress (e.g., the wp folder from Step 1).
- Theme Integration: Select “Yes” to apply your Magento theme’s header, footer, and CSS to your WordPress blog.
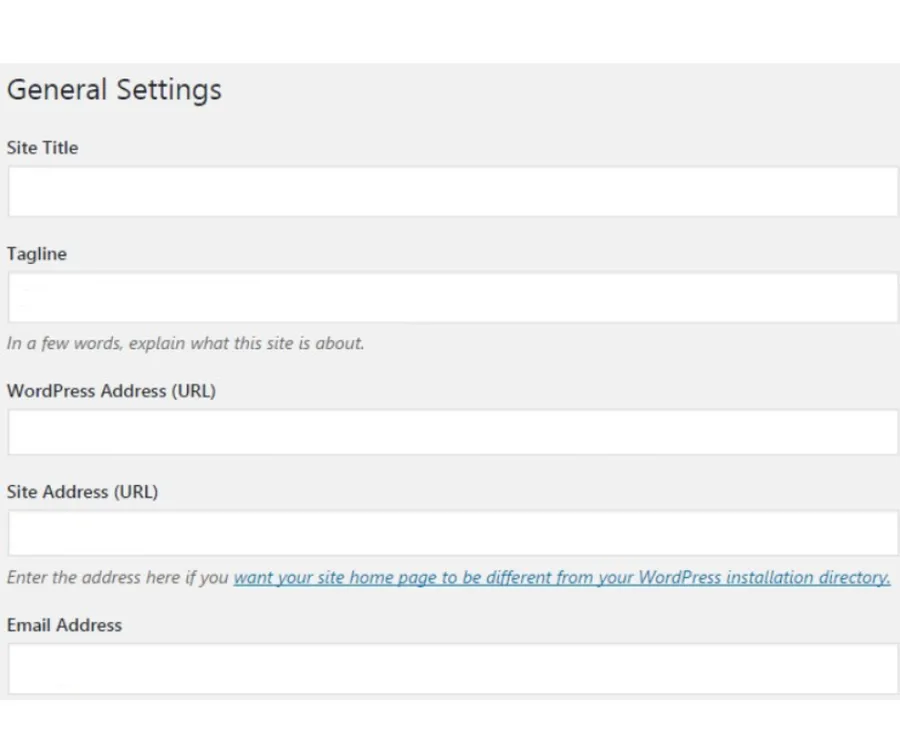
Step 4: Finalize URL Structure
To ensure your blog appears at yourdomain.com/blog rather than yourdomain.com/wp:
- Log in to your WordPress Dashboard.
- Go to Settings > General.
- Change the Site Address (URL) to your desired public URL (e.g., https://yourdomain.com/blog).
- Leave the WordPress Address (URL) pointing to the installation folder (e.g., https://yourdomain.com/wp).
Method 2 (Installing Magento on WordPress)
This method is suitable if you have a high-traffic WordPress site and want to introduce product sales without rebuilding your site on Magento from scratch.
Prerequisites
- An existing WordPress website.
- A Magento installation (even if basic).
- Both installations must usually share the same database server to facilitate data sharing.
Step 1: acquire a Connector Plugin
You will need a specific plugin designed to pull Magento blocks into WordPress, such as M2WP or similar API-based connectors.
Step 2: Install the Plugin on WordPress
- Log in to your WordPress Admin Dashboard.
- Navigate to Plugins > Add New.
- Click Upload Plugin and select the zip file you downloaded.
- Click Install Now and then Activate.
If you’re new to WordPress, you can follow this beginner-friendly guide on how to install WordPress plugins step by step to complete the process correctly.
Step 3: Configure the Connection
- Navigate to the plugin settings page within WordPress.
- Enter your Magento database credentials or API keys as requested by the specific plugin.
- Map your Magento static blocks to your WordPress widget areas.
Note: This method is technically complex. If you are not comfortable managing databases or PHP code, it is advisable to consult with a developer.
FAQs About Magento WordPress Integration
What is Magento WordPress integration?
Magento WordPress integration is the process of linking the Adobe Commerce (Magento) eCommerce engine with the WordPress content management system. This allows businesses to use Magento for powerful product and checkout management while utilizing WordPress for superior blogging, SEO, and content marketing features—all under a single domain and brand design.
Why should I integrate Magento with WordPress?
Integrating these platforms provides the “best of both worlds.” You gain Magento’s high-level security and scalability for transactions and WordPress’s intuitive interface for content creation. Key benefits include improved organic search rankings, a more engaging user journey, and the ability for marketing teams to update the blog without technical assistance.
Which integration method is best for my business?
The best method depends on your site’s primary focus:
Method 1 (WordPress on Magento): Best for established stores where eCommerce is the core focus and you want to add a professional blog to your subfolder (e.g., /blog).
Method 2 (Magento on WordPress): Best for content creators or publishers who already have a massive WordPress audience and want to start selling products managed by a Magento backend.
Do I need a developer to connect Magento and WordPress?
While basic plugins like FishPig simplify the process, a developer is often needed for advanced theme synchronization, Single Sign-On (SSO) setup, or resolving server-level conflicts. If you are not comfortable with SSH commands or database management, professional help is advised.
Conclusion and Recommendations
Deciding to integrate Magento with WordPress is a smart move for any digital business looking to scale content and commerce simultaneously.
- Choose Method 1 if your primary business is selling products and you need a blog to support marketing efforts. This is the most stable and popular configuration.
- Choose Method 2 only if you are a content publisher first and want to experiment with selling merchandise without migrating fully to an eCommerce platform.
By following this Magento WordPress integration tutorial, you can eliminate data silos and create a unified, high-performing website that satisfies both search engines and shoppers.
Read more: Magento Vs PrestaShop – Which One Is Best For You?
Contact US | ThimPress:
Website: https://thimpress.com/
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/ThimPress
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/c/ThimPressDesign
Twitter (X): https://x.com/thimpress_com



