Is your website invisible on Google?
Don’t worry — it simply means Google hasn’t indexed your pages yet. In this complete guide, you’ll learn 12 proven ways to index your website on Google fast.
Whether you’ve just launched a new site or noticed that your pages are missing from search results, these methods will help you make Google crawl, discover, and index your website quickly and effectively.
Eduma – Education WordPress Theme
We provide an amazing WordPress theme with fast and responsive designs. Let’s find out!
Google Indexing Terms
What are Index, Crawl, Crawler, Googlebot, and SEO?
Here is a brief dictionary of key terms used in this guide:
Index
Google keeps an index where it keeps data on websites it is aware of.
Each index item contains information such as the page’s content and URL.
When Google receives a page, examines its content, and adds it to the index, this is referred to as indexing.
Crawl
This is the procedure for looking for recently updated or new web pages.
Google finds URLs by using a variety of techniques, including links, sitemaps, and other techniques.
It entails Google actively searching the internet for new pages that will eventually be indexed.
Crawler
The automated software used to fetch and index online pages is referred to as a crawler.
It navigates the internet, retrieves webpages, and stores them in the index.
Googlebot
The general name for Google’s crawler is Googlebot or Web Spider.
Continuously researching and gathering data from online sites, it crawls the internet.
SEO
The process of SEO entails making changes to your website in order to increase its exposure and functionality in search engines.
It includes a range of methods and tactics intended to raise the position of your website in search results.
Why do you need to get Google to index your website faster?
So why do you need to get Google to index your site faster?
Indexing and ranking in a music competition are analogous to registering and competing in a competition.
By registering, you become eligible to enter and compete in the competition.
The organizers of the competition must keep track of your participation, just like search engines index web pages.
The ranking phase evaluates your performance, similar to how search engines rank pages based on relevance.
Just as a website that is not indexed cannot be ranked, you cannot compete if you do not register.
While rating affects your placement and chances of winning, registering allows you to participate.
In summary, ranking is analogous to grading and placement, while registration is analogous to indexing.
How to Find Out if Google Has Indexed Your Website
Google searches the web automatically to find and index websites.
In most circumstances, you don’t need to do anything other than make your website available online.
However, specific sites may be excluded from the search index on occasion.
To secure your website’s existence on Google and improve its visibility in search results, check to see whether it’s indexed and investigate ways to make your content more visible in Google Search.
Check to See if Your Website is Indexed by Google
Use your site’s home URL to search for “site:” to see if Google has indexed your website.
It’s a sign that your website is indexed if you come across pertinent results.
As an illustration, results from a search for “site:thimpress.com” will show that the website is indexed. This figure is an approximation of the number of pages from your website that Google has indexed.
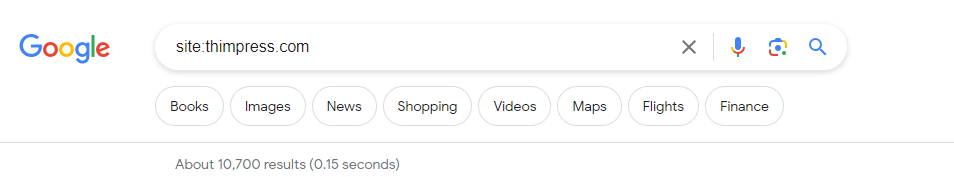
You may use the same operator to determine whether a specific URL is indexed: “site:yourwebsite.com/web-page-slug.”
For example, results from a search for “site:thimpress.com/what-is-seo” will show that the website is indexed.
This will assist you in determining whether or not Google has indexed that particular web page.
Why is my website not indexed?
There are a number of reasons why Google could not have indexed your website, You can refer to the main reasons given by Google and some common reasons that websites often encounter:
- Insufficient connectivity: If your website has few external links, Google crawlers may have difficulty finding and indexing it.
- New website: If you recently created your website, it may take some time for Google to crawl and index it. Be patient.
- Crawlability issues: Your website’s layout or design may make it difficult for Google to crawl and index its content efficiently. This could be due to technical issues such as poor URL structure or unavailable content.
- Crawl errors: Errors prevented Google from successfully crawling your website, preventing proper indexing. These errors could be caused by a malfunctioning server or other technical issues.
- Policy-based blocking: Google may be unable to crawl and index your website due to a robots.txt file or other directives on your website. Check your website’s settings to ensure there are no unauthorized blocks.
Also here are detailed examples of the reasons why Google doesn’t index your website.
Image taken from Google Search Console:
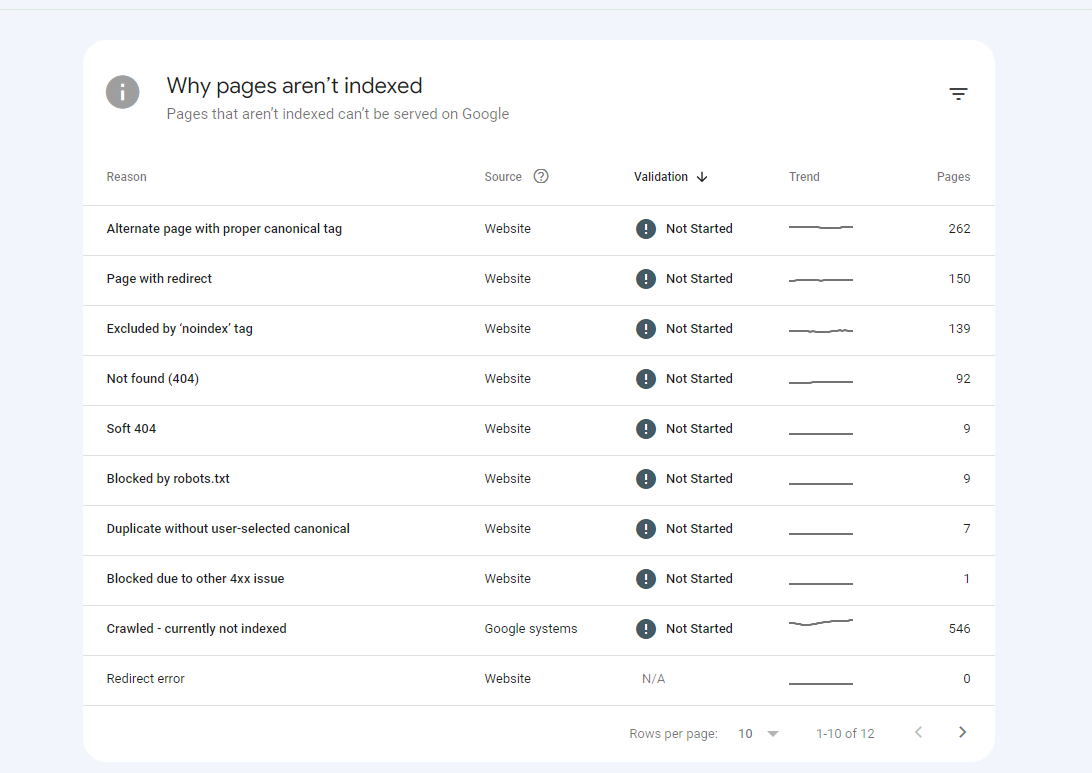
It is crucial to note that if you use Google Search Console, you have the choice to use the coverage page report to get a more exact idea of how well your website is indexed.
You can easily find it here: Google Search Console > Pages
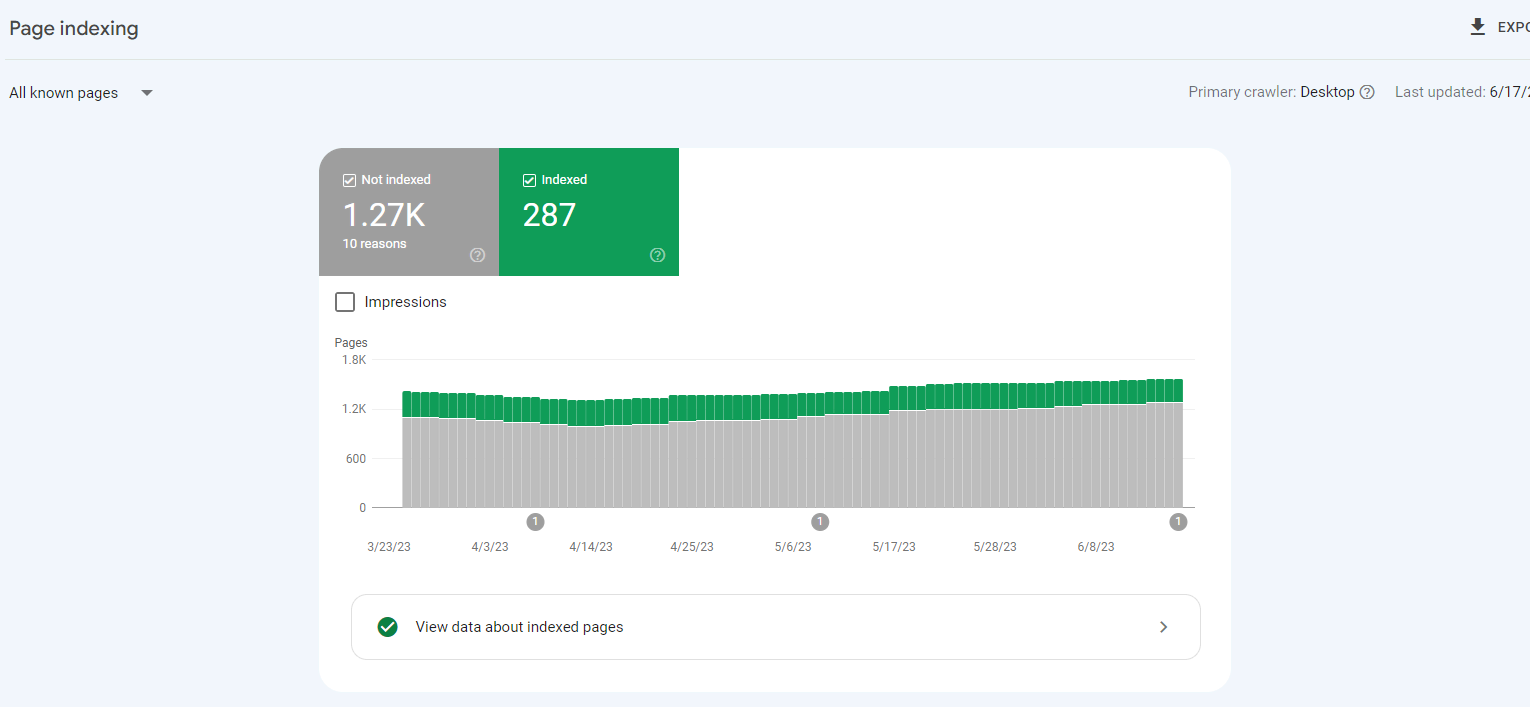
If the sum of these two values is more than zero, Google has at least partially indexed some of the pages on your website.
If the sum is 0, there is a serious problem because none of your web pages are being indexed.
A page’s index status can also be checked using the Search Console.
Enter the URL in the URL Inspection tool by simply pasting it.
The notice “URL is on Google” will appear if the page has been indexed:
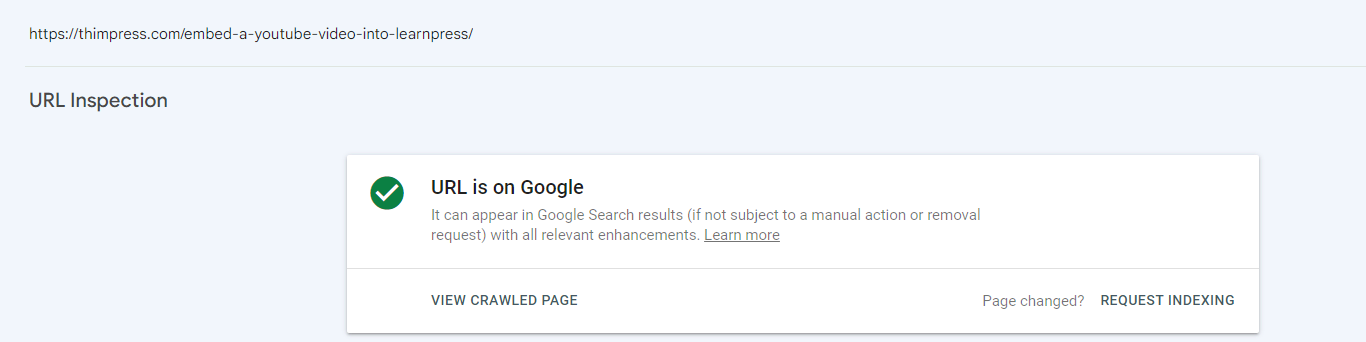
The words “URL is not on Google” will appear if the page is not indexed:
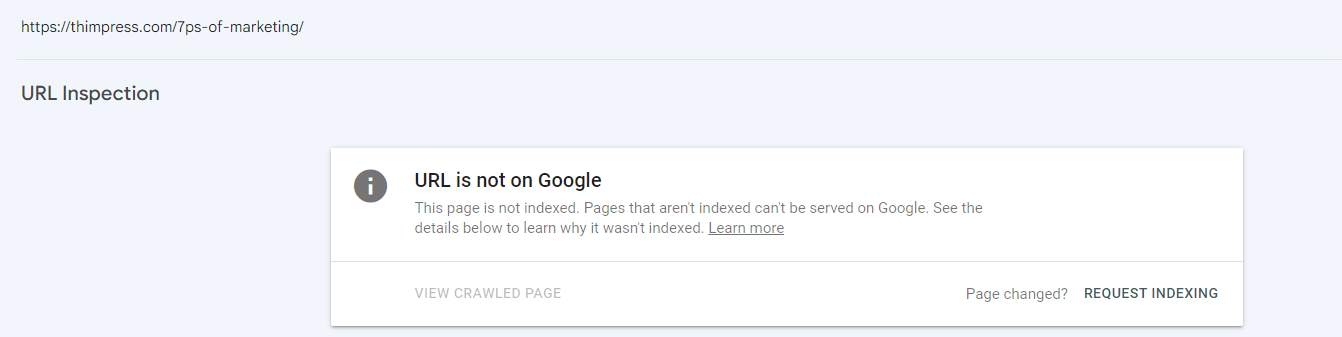
The 12 Best Ways to Get Your Website Indexed by Google
We have a better understanding of the terms that Google often uses in indexing, and also know how to request index. So, how to get google to index my site faster? Let’s find out with ThimPress right here.
Create High-Quality Content that Complies with Google Policies
Make sure the content of the website you provide complies with Google’s standards, meaning it doesn’t fall into the spam category, before trying any additional methods to get your site indexed faster by Google.
Typical fundamental mistakes that will prevent Google from indexing your website are:
- Inaccurate content: Publishing content that is misleading or deceptive, or that does not match the title or description of the page. For example, a page titled “How to Lose Weight” is actually full of ads for weight loss products.
- Malicious website: Hosting malware or phishing scams on your website.
- Keyword stuffing: Overusing keywords in your content in an attempt to manipulate search engine rankings. For example, a page about “dog food” repeats the phrase “dog food” hundreds of times.
- Spam links: Buying or selling links to your website or engaging in other link building schemes that violate Google’s guidelines.
- Fake traffic: Using bots or other methods to generate artificial traffic to your website.
- Content duplication: Copying content from other websites without adding any unique value.
- Automatically generated spam content: Programmatically generated content with the sole purpose of manipulating search engine rankings. This type of content is often low-quality and irrelevant to users.
Tips: Google is aware that the online advertising and sponsorship industries frequently engage in the buying and selling of links. It is not against Google’s rules as long as these links are suitably marked with the rel=”nofollow” or rel=”sponsored” attribute value in the <a> tag.
In summary, ensuring visitors to your website have the best experience possible should be your first concern.
Consider what makes your website special, valuable, or interesting.
Use the self-assessment questions in our guide to producing information that is helpful, trustworthy, and emphasizes individuals to make it simpler for you to judge your own work.
Google recommends content that includes photographs and videos to increase indexing on the page and to improve the user experience.
You can prioritize using video to do this.
If your website performs well with high-quality content, Google will appreciate it and give it priority indexing.
Claim Your Business Profile on Google Business Profile
Another simple but extremely effective way for Google to index your website more easily is to determine the legality of that website. Google Business is an indispensable choice for your business.
The following advantages for the Google index are provided by claiming your business profile on Google:
- More visibility in Maps and Search.
- Increased control over your corporate data.
- Enhanced customer experience with precise information.
- Credibility and trust for your brand.
- Optimization for local search to increase visibility locally.
Submit Your Page to Your Sitemap for Better Google Indexing
A sitemap acts as a roadmap for Google, highlighting the significance of certain pages on your website and how frequently they should be crawled.
Even though Google can still find pages on your website without them being in the sitemap, it is still best practice to include them.
After all, there is no need to obstruct Google’s workflow.
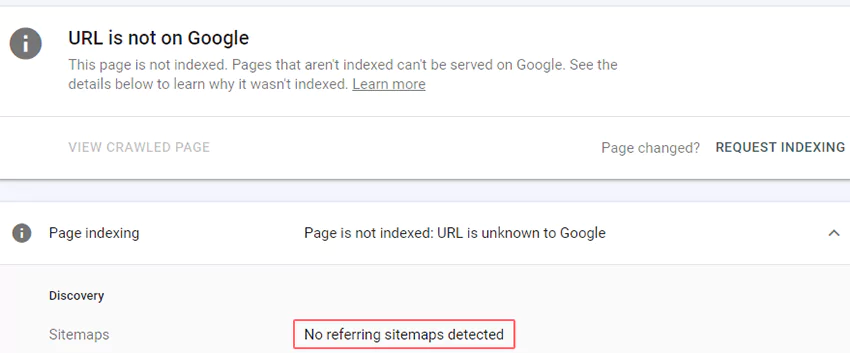
Use the URL inspection tool in the Search Console to check whether a page is included in your sitemap.
The “URL is not on Google” problem and “Sitemap: no referring sitemap detected” message means that Google has not indexed the page and neither has your sitemap.
If you choose not to use Google Search Console, there are a ton of alternative ways to add pages to your sitemap, but let’s face it—we’re trying to index your website at any cost—so don’t ignore Google Search Console.
Enhance Website Security to Meet Google Standards
Make sure to check to see if any security vulnerabilities with your website have been reported.
These errors could lower your page’s score and possibly result in browser and search result warnings. The Security Issues report will provide helpful advice on how to correct any manual steps needed.
You can also refer to the web.dev page listed below for guidance on boosting security by Enabling HTTPS on your servers.
If you use WordPress, you might want to look into these well-known and acclaimed security WordPress plugins.
These plugins have the capacity to find security flaws in your website’s code, fix problems, and offer suggestions for enhancing your website’s security.
Optimize Your Website for Speed and Responsiveness
Speeding up your page load and improving accessibility on all devices is what you need to do to make it easier for Google to index your website;
If your website is using non-responsive code or outdated framework, we recommend updating and optimizing to ensure the loading speed of the website.
Google’s index can gain a number of advantages by optimizing material for mobile, including better mobile indexing and more exposure in mobile search results.
This can be accomplished by employing responsive code, hence it is suggested that WordPress users choose a responsive WordPress theme.
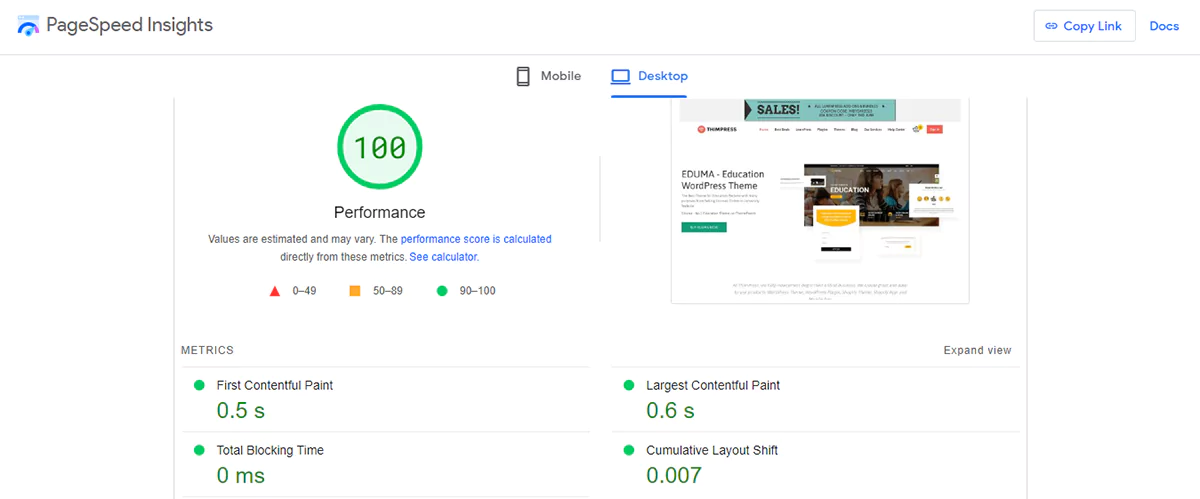
You can check your page loading speed at PageSpeed Insights, and PageSpeed Insights will also highlight factors that are slowing down your page speed.
Remove Crawl Restrictions in Robots.txt File
Do you have issues getting your full website indexed by Google? It’s possible that a crawl restriction in the robots.txt file is to blame.
Visit example.com/robots.txt, substituting “example.com” with your own domain, to see if this is the problem.
Look for the following lines of code:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /Alternatively, you may come across these lines:
User-agent: Googlebot
Disallow: /Googlebot is informed by both of these code snippets that it is not permitted to crawl any pages on your website. Simply delete these lines to remedy the issue.
A crawl block in the robots.txt file may also be to blame if Google isn’t indexing a particular webpage.
Use Google Search Console’s URL inspection tool to see if this is the case.
To obtain further information, paste the URL of the issue page and click the page block.
Look for the error message that says “Indexed, though blocked by robots.txt”
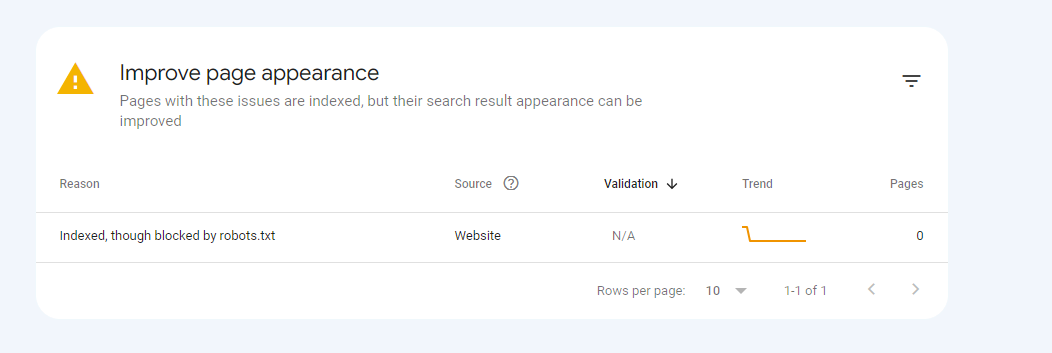
This shows that the robots.txt file is blocking access to the page.
If so, check your robots.txt file for any “disallow” directives that might apply to the page or any associated subsections.
Additionally, it’s a good idea to set up your robots.txt file to stop Googlebot from crawling crucial pages. For instance:
User-agent: *
Disallow: /wp-admin/Also, if you still have trouble editing the robots.txt file, I recommend you refer to the official Google article on How to write and submit a robots.txt file.
Simplify Your URL Structure for Better Google Indexing
The usability and search engine optimization of a website depends heavily on maintaining a straightforward URL structure.
Here are some suggestions to help you do that:
Use Clear and Readable Words in the URL. Instead of long ID numbers, incorporate descriptive words that accurately represent the content of the page.
For instance:
https://thimpress.com/wordpress/themes/Maintain Logic and Consistency. To make it simpler for people to navigate and comprehend the organizational structure of your website, make sure the URL structure follows a logical hierarchy.
For instance:
https://thimpress.com/category/glossaryKeep URLs Short. Avoid creating URLs that are too long since they could confuse people or be difficult to distribute. Try to create URLs that are brief, relevant, and appropriately reflect the content.
For instance:
https://thimpress.com/internal-link-building-plugins/To maintain optimal URL structure, avoid the following:
- Non-ASCII characters in URLs
- Unreadable, long ID numbers in URLs
- Underscores (_) in URLs (e.g., “https://thimpress.com/wordpress_theme”)
- Words joined together in URLs (e.g., “https://thimpress.com/wordpresstheme”)
Following these guidelines will ensure that your URLs are user-friendly and adhere to Google’s recommendations.
Additionally, if the website’s URL changes, make sure you redirect the old URL to the new one.
Also, after updating the URL, make use of Google Search Console to index it.
Build a Strong Internal Linking Structure for Better Google Indexing
By applying an internal link building strategy to your website, you may make it simpler for Googlebot to understand the information across the website, which will speed up the indexing of your page.
Take a page with important content as an example.
Since Google has previously indexed the page and finds it useful, using it as a related link for a post with content related to it will help Google better understand the content of the post and have more grounds to index it.
Building internal links also serves the function of informing Google that the information is essential because there are numerous websites that link to it.
As a result, Google will index pages with important content first and less important stuff second. You can share this power straight on your page/post page by using “powerful” related links.
You can implement your internal link plan using the helpful internal link building tools we’ve reviewed.
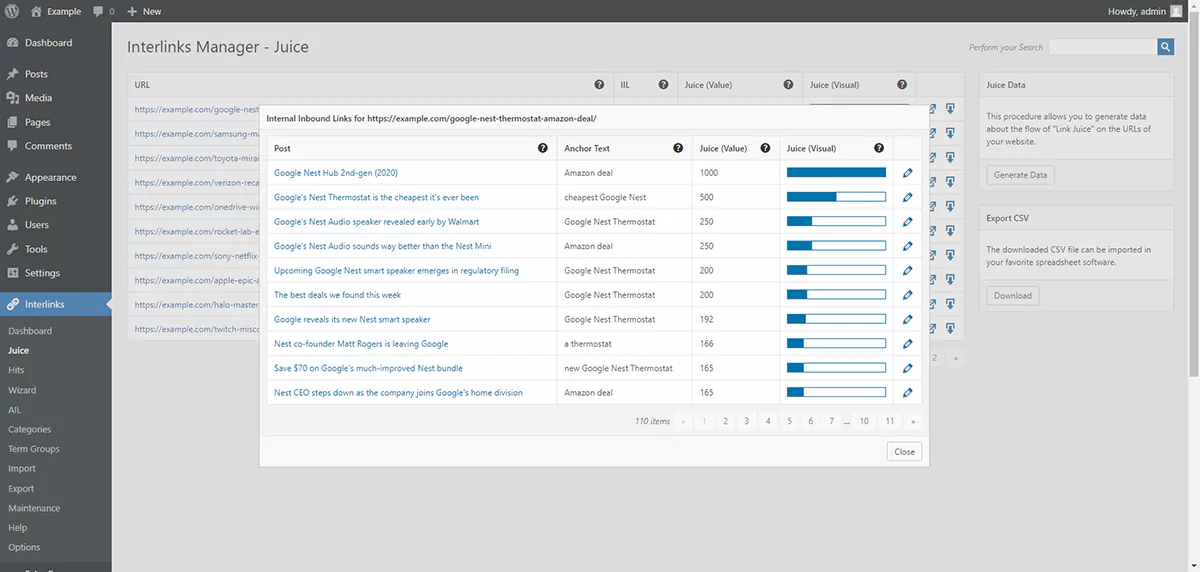
Create High-Quality Backlinks to Boost Google Indexing
Backlinks are a key factor in assessing how important a web page is to Google.
Links from other websites point to a page, indicating its importance and significance.
Google gives these pages priority while indexing them.
The question here is what is a quality backlink?
We will evaluate the quality of backlinks based on Google’s algorithm.
A quality backlink is a dofollow link pointing to a page on your website that is highly valued by Google (Which is determined by 5 main factors: Meaning, Relevance, Quality, Usability, and Context), ranks highly in the search results, and is relevant to your topic.
It’s vital to remember that indexing factors other than backlinks also play a role. Google indexes a lot of pages without backlinks, but the importance of pages with good links is higher.
Since Google prefers to crawl and re-crawl such pages more quickly, indexing is completed more quickly.
Use Googlebot-Friendly Tag and Anchor Text
Google typically uses the HTML element, also known as the anchor element, with a href property to crawl and extract links.
Google’s crawlers often do not parse and extract links in different forms.
Due to script events, Google has trouble accurately retrieving URLs from elements without a href property or other tags that serve as links.
Let’s look at some links that Google can parse and those that it cannot.
Here is an example of recommended link usage:
<a href="https://thimpress.com">Conversely, here are examples of link usage that are not recommended:
<a routerLink="wordpress/themes">
<span href="https://thimpress.com">
<a onclick="goto('https://thimpress.com')">When it comes to using links on blog posts, one of the most important factors is Anchor text;
Google can recognize the anchor text and rank the links associated with that anchor text to see if the links are really relevant.
Avoid using too general words like Read More, Click Here, Our Website, etc., and a sentence that is too long for anchor text.
Remove Low-Quality Content to Improve Google Indexing
The Crawl Budget will be wasted if your website contains too many poor-quality pages. In line with Google’s recommendations:
When server resources are dedicated to poor-quality web pages, crawl activity is diverted away from finding important information on your website. High-quality web pages may take much longer to find and index as a result of this.
Think of a library that has a huge selection of books. It is more difficult for the librarian to display the wide variety of books available if many copies of the same book are taking up shelf space.
To give library patrons a more satisfying experience, the librarian may place a higher priority on presenting uncommon books.
Google agrees that some degree of duplicate material is unavoidable and frequently required, but overdoing it can hurt your search engine rankings.
Focusing on creating and disseminating unique, high-quality content is crucial if you want to increase your website’s visibility and search engine rankings.
Audit Your Website’s Content to Improve Google Indexing
The website’s overview content is periodically crawled and re-crawled by Google;
Therefore, auditing and changing the content of the entire website so that it is optimized for SEO can increase authority and increase the possibility of being indexed by Google.
There are 5 elements on each page that should always be optimized for better Google indexing:
- Page title.
- Page slug.
- Page headings (H1, H2, H3, etc.).
- Meta description.
- Images (image alt, image title, image size, etc.).
A website’s chances of getting indexed by Google and other search engines can be increased by improving these criteria;
It boosts a website’s exposure in search results, encourages organic visitors, and could perhaps raise a site’s authority and ranking in search engine indexes.
If you’re not sure where to begin, consult the best tools for finding pages or posts that need auditing, such as SEMrush and Ahrefs.
These 2 tools can identify websites that require improvement or removal in order to maintain the crawl budget.
Common Reasons Google Isn’t Indexing Your Site
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| “Crawled — not indexed” | Low-quality or duplicate content | Improve content depth |
| “Blocked by robots.txt” | Misconfigured robots.txt | Allow access to key pages |
| “Discovered — not indexed” | Too many low-value URLs | Consolidate or delete weak pages |
| Missing sitemap | No crawl path | Submit sitemap via Search Console |
Conclusion: Make Google Index Your Website Fast
Getting your website indexed by Google is not as hard as it seems.
By following these 12 proven techniques, you’ll make sure your site is crawled, indexed, and ready to appear in Google Search results quickly.
Stay consistent with high-quality content, monitor Search Console regularly, and optimize your pages for user intent.
Soon, you’ll see your pages appear in search — bringing in real organic traffic.
FAQ: Google Indexing Guide
Q1: How long does it take for Google to index my website?
It can take from a few hours to several weeks, depending on your site’s authority and how often Google crawls it.
Q2: Why is my website not showing up on Google?
This usually happens when Google hasn’t crawled your site yet or your robots.txt blocks important pages.
Q3: How can I make Google index my site faster?
Request manual indexing in Search Console and build internal/external links to boost discovery speed.
Contact US | ThimPress:
Website: https://thimpress.com/
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/ThimPress
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/c/ThimPressDesign
Twitter (X): https://x.com/thimpress_com



