Search engines use web crawlers, also known as spiders or bots, to explore billions of web pages. These robots move around the internet by following links and finding new pages. They gather these pages into a database called an index so that they can be searched later.
When people search for something, the search engine looks in this index for matching information. To give the best results, the search engine’s algorithms check things like how relevant and good the information is. Then, it shows the most fitting results to the user.
In this article, we will explain and guide you through How search engines work step by step and give suggestions for each heading related to how search engines work.
Search Engine Fundamentals
First, let’s start with the basic concepts of search engines, such as what they are and what they aim to do. After that, we’ll take a closer look at how they actually work.
What is: Search Engine?
A search engine is a software that finds web pages related to what you’re looking for. It looks through the internet for specific information based on what you type into the search bar.
The results usually show up on a page called the search engine results page (SERP). You might see links to websites, pictures, videos, articles, and more. It’s a mix of different kinds of information that match your search.
Simply put, a search engine is like a big library of web content that you can search through. It has two main parts:
- Search index: This is like a catalog of information about websites.
- Search algorithm: It’s a type of computer software that matches what you’re looking for with the information in the search index.
Note: The search index holds discovered website links and important clues, like keywords in the website’s content, the type of information identified using Schema, how recent the page is, and what users did on the page before. These details help us understand what each website is about and how users interact with it.
What is the Goal of a Search Engine?
Now, let’s talk about what search engines aim for, both for the people searching and for the ones running the search engine.
Search engines optimize for search engine users. Search Engines can be seen as a product. The goal of any product is to reach the right customers and solve their problems. Therefore:
- Search Engines are improved to be highly accurate and suitable for users.
- Search Engines aim to offer the most fitting results to users.
Search engines earn money by using paid search services. When customers have their needs fulfilled, companies gain more customers, expanding their market share. This success leads to the creation of a service called “Paid Search.” In this service, the search engine offers two types of search results:
- Organic results: These listings are free and appear because they match someone’s search words.
- Paid results: Non-organic results are ads that you pay for to appear in these spots.
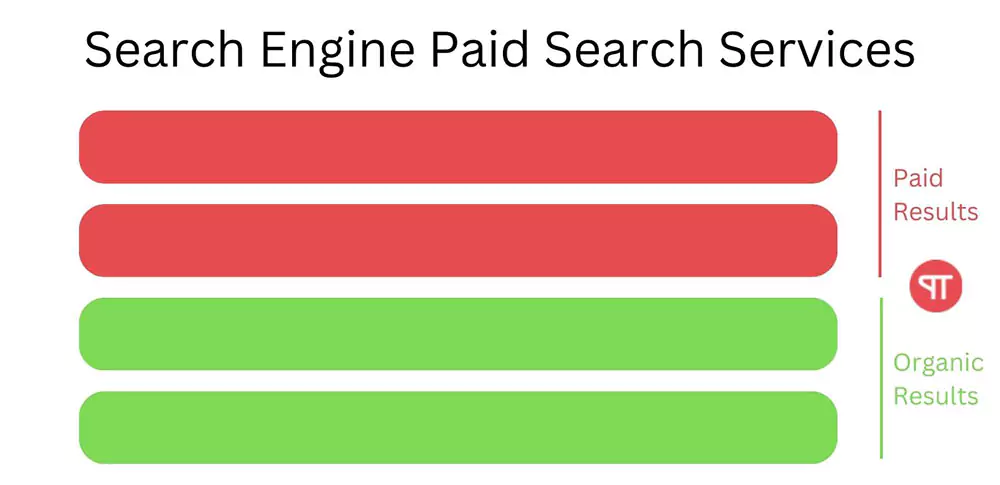
The advertiser pays the search engine for every click on a paid search result. This type of advertising model is called pay-per-click (PPC). This highlights how having a bigger user base is crucial because more users mean more clicks on ads, resulting in higher revenue.
Market share of search engine
In May 2023, according to data from SimilarWeb, Google holds the highest global search engine market share at 90.80%. Yahoo follows with 3.21%, Bing with 3.04%, Naver with 0.46%, Yandex with 0.36%, and other search engines at 2.12%.
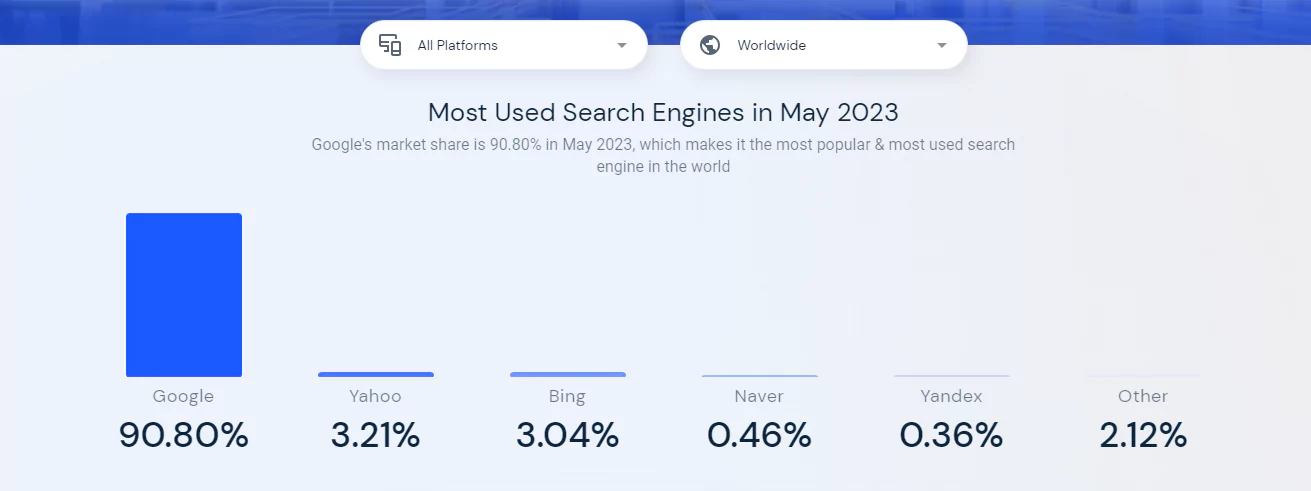
We can see that Google’s search engine occupies almost all the market share, and the number of using other search engines is negligible. So in this article, we will focus on analyzing how the Google search engine works.
How Google Search Engine Builds Its Search Index
We now know how search engines work. Since Google is widely used, let’s focus on how it builds its search index, going through the steps one by one.
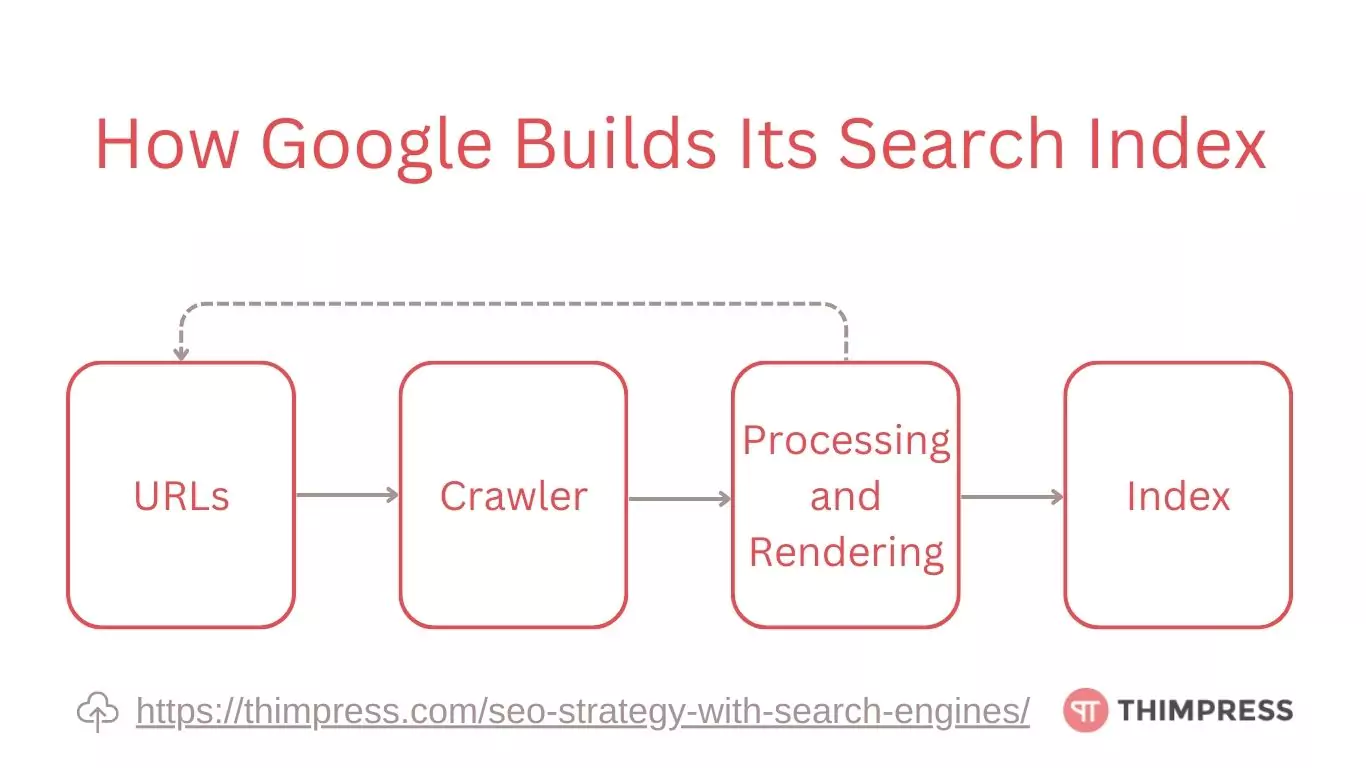
Search engines collect URLs
Google’s Search Engine uses various methods to find website URLs. Here are the most common ways:
- Direct Crawl: Google’s spiders visit websites and discover URLs without needing external signals.
- URL Submissions: Site owners can request Google to crawl specific URLs through Google Search Console.
- Internal Links: Google follows links within a website to find new URLs.
- Social Media: Google’s spiders find URLs on social media platforms.
- News and RSS Feeds: Google scans news sites and RSS feeds for new stories and webpages.
- URL Canonicalization: Google identifies different URL variations (e.g., with or without “www”) and combines them into a single canonical URL.
Search engines crawl page element
Googlebot, the crawler behind Google Search, dives deep into web pages to understand their meaning. It accomplishes this by fetching their HTML code and scrutinizing key components like text, images, headings, and links. This in-depth analysis allows Googlebot to accurately index pages and rank them relevantly for your searches.
For example. Clear headings and descriptive alt text for images help Googlebot grasp the page’s core message, making it more likely to appear when you need it.
Processing and rendering
Google’s web crawlers go beyond just downloading pages. They delve deeper, parsing HTML code, analyzing data structures, and understanding the meaning of words using sophisticated natural language processing.
This even involves rendering the page to mimic how users see it, helping Google decipher layout, user interaction, and dynamic content.
While the full recipe is Google’s secret sauce, we know they extract vital information like text, links, and structured data.
This vast amount of data is then indexed, meticulously organized, and constantly updated, creating a colossal knowledge base at our fingertips.
The payoff? When you search for something, Google can serve you relevant results in a blink, all thanks to this intricate web-processing power.
Indexing into digital collection
Deep within Google’s core lies a sprawling labyrinth of knowledge – the index. This behemoth houses information about countless websites, each entry meticulously organized with details like text snippets, titles, and even images.
It’s not just a passive storage vault; the index is a living, breathing entity, constantly updated as Google’s crawlers explore the web.
When you embark on a search, you’re not just typing into a void. You’re triggering a dance of algorithms, with the index at the heart of the action.
Google dives into this labyrinth, analyzing content, understanding meaning, and pulling out relevant entries like a master librarian. Imagine it as a library containing billions of books, each with clear labels and helpful summaries, ready to guide you to your information destination.
That’s the power of the Google index – a testament to the magic behind every search.
Remember: If your site isn’t in the index, it won’t show up in searches! It’s crucial to be listed in search engine indexes like Google and Bing so that users can find you. Make sure Google indexes your website for better visibility.
How Google Search Engine Rank Pages
Google ranks pages in search results using its algorithms. Since Google’s algorithm is very complex and constantly evolving, it’s not advisable to delve too deeply into analyzing or applying it.
However, we can focus on creating content based on what the search engine algorithm values, which are Authority and Relevance. Aim to produce material that showcases your expertise (Authority) and aligns well with what users are searching for (Relevance).
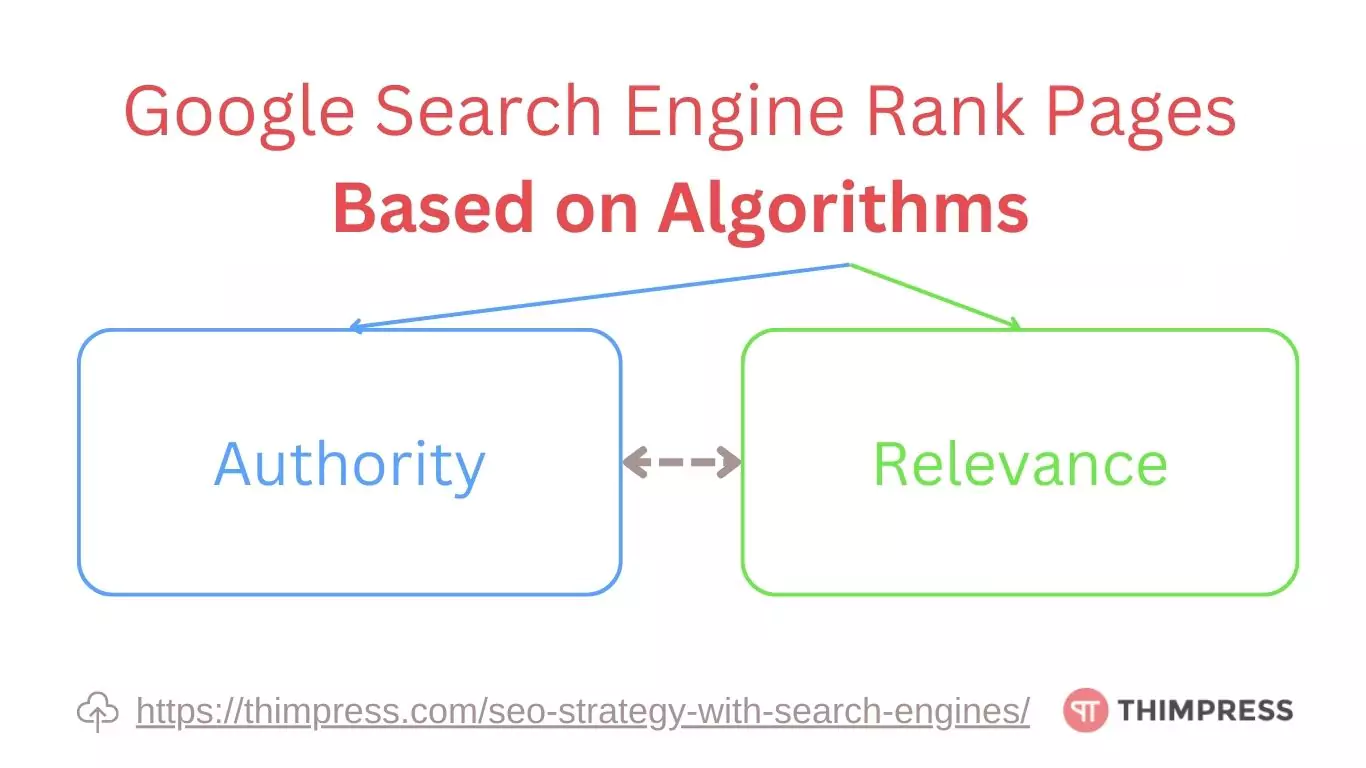
Authority reflects the reliability of the website
Search engines use various factors to evaluate a website’s domain authority. Domain Authority is a metric that reflects a domain’s overall reputation and trustworthiness. While search engine algorithms are kept secret and not publicly available, some important traits are often taken into account:
Backlinks. Building a strong web presence begins with earning backlinks, valuable links from other websites pointing to your domain.
Think of them as votes of confidence, telling search engines your site is worth visiting.
Earning links from reputable sources like industry leaders or relevant blogs boosts your domain authority, a measure of your website’s trustworthiness and influence in the eyes of search engines.
While building backlinks organically is a strategic task, content marketing, guest blogging, and creating shareable infographics can attract attention and encourage citations.
SEO tools like SEMrush can offer valuable insights into competitor strategies and your own backlink profile, helping you build a winning link profile.
Don’t underestimate the power of social media. While likes and shares may not directly impact domain authority, they can amplify your content’s reach and attract more visitors, potentially leading to those coveted backlinks.
Remember, backlinks are like trusted recommendations for your website, and cultivating them paves the way for attracting organic traffic and establishing your online authority.
Content Quality. Search engines, the gatekeepers of information, scrutinize your website’s content, evaluating its quality and relevance to determine who deserves the coveted top spots. So, how can you ensure your content shines brighter than the rest?
- Write for Humans, Not Machines: Forget keyword stuffing and robotic prose. Search engines are getting smarter, prioritizing content that engages and informs users. Write in a clear, concise, and natural style, addressing your audience’s needs and pain points.
- Focus on Value, Not Fluff: Each piece of content should offer something unique and valuable. Conduct thorough research, present insightful arguments, and provide actionable tips. Don’t just regurgitate information; add your own perspective and expertise.
- Embrace Uniqueness: Plagiarism is a cardinal sin in the content world. Use your own voice and creativity to stand out from the crowd. While inspiration is welcome, ensure your content is original and reflects your brand’s identity.
- Images: The Visual Spark: Images not only break up text and enhance readability, but they can also boost engagement and search engine visibility. Use high-quality visuals relevant to your content, optimize them for speed, and include alt text for accessibility.
- Embrace the Power of Originality: Aim for at least 90-95% unique content. This doesn’t mean reinventing the wheel, but rather building upon existing knowledge and adding your own valuable insights. Use plagiarism checkers as a helpful tool, but remember, true originality comes from your own creativity.
Pro Tips: quality content is an investment that pays off in the long run, attracting more visitors, building trust, and ultimately, achieving your online goals.
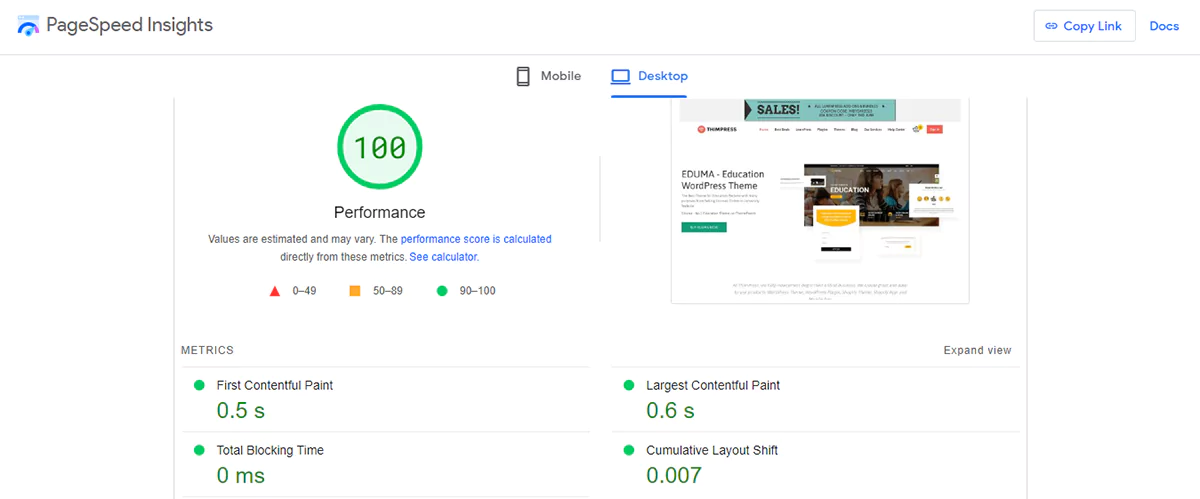
User Experience. User experience factors such as website load speed, mobile responsiveness, and overall usability can all have an indirect impact on domain authority.
Search engines prioritize user-friendly websites. Use the PageSpeed Insights tool to determine your site’s speed and how to address the issues that are slowing it down.
In case you use WordPress. You may also choose WordPress themes for yourself that are compatible with all types of devices by consulting the list of the best responsive WordPress themes.
Domain Age and History. Older domains with a longer history tend to have greater authority because they have had more opportunities to gather backlinks and create a reputation.
Furthermore, the history of a domain, including any previous penalties or spammy conduct, might have an impact on its authority.
To further improve the security of your website, you should pick high-authority domain names like “.com” and “.net”.
These characteristics often play a role in determining a website’s domain authority, even though the exact algorithm details remain undisclosed.
Relevance reflects the website’s relevance to the content provided
Search engines employ complex algorithms to gauge the relevance of websites to specific search queries. These algorithms consider various elements to assess a web page’s content and context, estimating its relevance to particular search queries.
The following are some significant variables that search engines commonly utilize to determine relevance.
Keyword Analysis. The page title, headers, meta tags, and body text are all analyzed by search engines for the existence and placement of keywords. A page’s topic and relevance are better understood by search engines when relevant keywords and their semantic variants are present.
If you wish to write about a particular subject, you can use keyword analysis tools. These tools will provide you with related keywords as well as the historical search volume for those phrases. This makes it easier for you to write articles that are more concise and emphasize user search.
You can also refer to the “Related searches” section of Google.
Content Relevance. Relevance is the measure of how valuable a search result is to the person who conducted the search. For the purpose of determining relevancy, search engines like Google use a variety of techniques. Fundamentally, they look at web pages with terms that match the search term. Search engines also look at user interactions to see if other users found a certain result useful.
Page Structure and Formatting. Search engines may better comprehend how a web page is organized and arranged by using headings, subheadings, bullet points, and paragraphs in its structure and style. The relevancy of the page is increased by its organized and logical structure.
A helpful tip is to make sure your blog article has a hierarchical structure and distinct headings. Start with a single main heading (H1), then add more detail using subheadings (H2) after that. Use subheadings (H3) to add more information or clarification under the corresponding subheadings (H2) if necessary. And don’t forget to put your keywords in the title to increase relevancy.
Your search engine optimization (SEO) plan ought to include internal link building from a broader standpoint. This technique is essential for tying together your content and for developing a seamless narrative. You can increase the overall relevance of these pages to a certain topic and increase their visibility on search engines by linking relevant pages together.
Freshness. Search engines give new information the highest priority for specific sorts of requests. When determining the relevancy of a page, they take into account the page’s publication date and how frequently it is updated, especially for timely subjects like breaking news.
Regularly update your site’s high-view articles to ensure that your site doesn’t fall behind other “fresh kids”.
How Google Search Engines Personalize Search Results
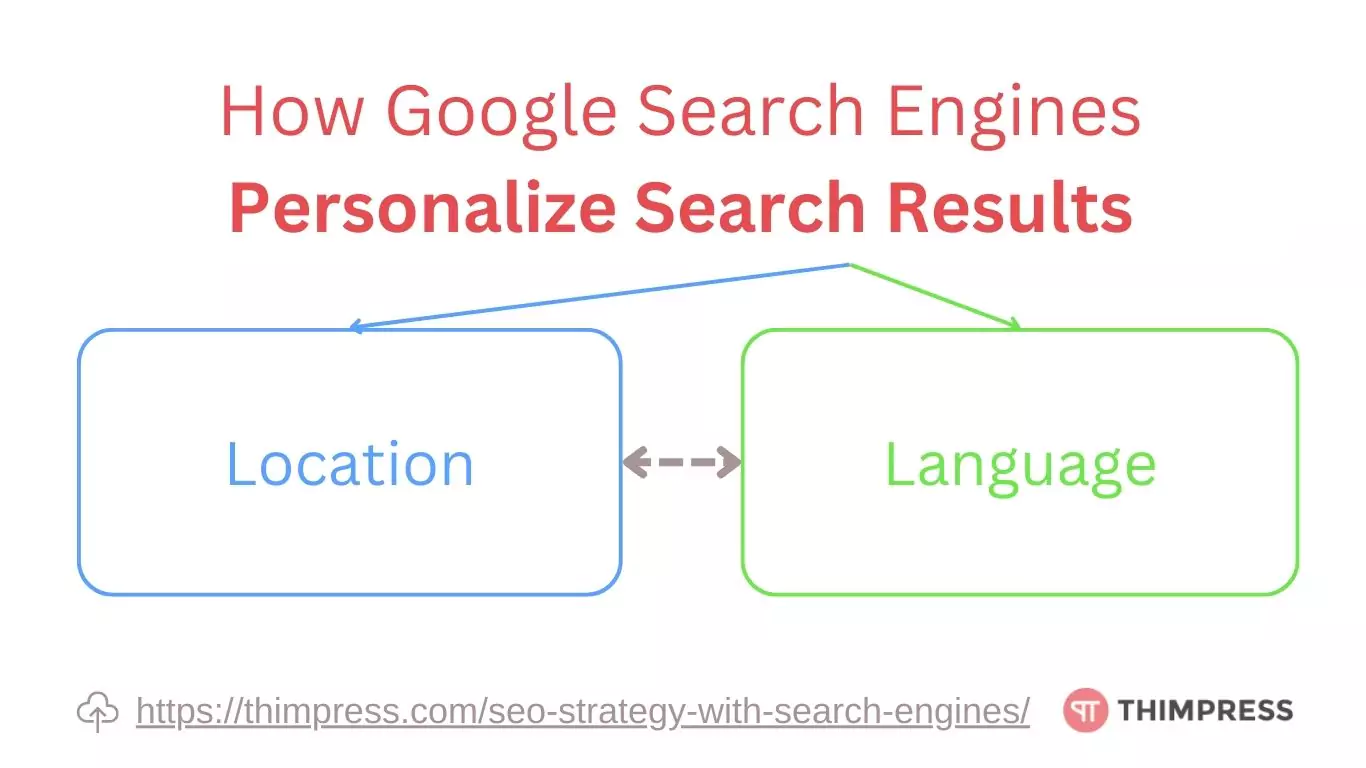
Location
Search engines strive to deliver particular results to a given place, especially for queries with a local purpose, such as “pet stores near me.” To comprehend the search’s geographic context, they consider the user’s IP address, GPS data, or other location markers.
Language
Search engines favor results that match the language of the search query after analyzing it. To make sure that the search results are in the same language as the user’s query, they also take the content language of the web page into account. Depending on their region or preferred language, search engines may offer results for multilingual users in a variety of languages.
Bonus: Search Suggestion
Google search engine can rely on your search history and based on the keywords you are entering suggest content related to the keywords you are searching for. In recent years, because of security for users, this feature has been limited, you can turn it on in the service settings of your Google account.
Build Your SEO Strategy with Search Engines in Mind
In conclusion, search engines use web crawlers to find and index online pages, which are ranked according to their relevance and authority.
As the top search engine, Google employs a number of techniques to locate URLs and makes use of its crawler, Googlebot, to scan and analyze web page information. Page rankings are influenced by elements like domain authority, backlinks, content quality, user experience, and relevancy.
Results are tailored by search engines based on language and region. It’s critical to comprehend these fundamentals and produce content that complies with search engine algorithms in order to develop a successful SEO strategy. This can increase web visibility and draw natural traffic.
Read More: WordPress For Education: A Comprehensive Guide
Contact US | ThimPress:
Website: https://thimpress.com/
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/ThimPress
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/c/ThimPressDesign
Twitter (X): https://x.com/thimpress_com



