Are you using WordPress as source code for your blog/website? So have you ever tried to learn about the history of the foundation and development of WordPress? Where did it come from and what are the key milestones noteworthy? If not, take a few minutes to find out.
Overview: The History Of WordPress
Used for millions of websites worldwide, WordPress is the most popular self-hosted open source today. Not only is excellence in the world of bloggers, but this system is also capable of powering all models of other websites. This includes several popular magazines and e-commerce website pages. So, do you wonder about the WordPress background?
The advantage of WordPress here is that it is entirely free. You can use it to create a simple website or a business website. Just go to the homepage of WordPress to download the latest version and install it. Then, you already own a website that can be easily customized, and it requires having a server, and a domain name.
However, WordPress still has a completely free service without those, wordpress.com solves that problem for you with some limitations are less customization and having to depend on WordPress servers.
The development of WordPress
The establishment stage
In 2003
First of all, Matt Mullenweg and Mike Little created WordPress in May 2003. They started building a blogging platform on a downed application b2/catalog. Not long after that, the project was abandoned, and they decided to fork it and continue to develop their own.
In 2004
In January 2004, they released the first version of WordPress (WordPress 1.0). It is very different from the content management system right now because you realize it has a lot of features.
However, it used to have only a few key features that we still use today, such as WordPress editor, easy installation, nice permanent link usage, user admin system, and comments management.
The development stage
WordPress history from 2004 to 2005
Since 2004, WordPress has undergone many major transformations. An open-source community with thousands of members continuously developed, managed, and operated the WordPress project. They work remotely, many are volunteers.
Moreover, they meet at a conference called WordCamp. WordPress is still on the rise and a new version is usually released every 2 or 3 months. Each version has new features added and security updates.
The first version of WordPress that supports plugins was version 1.2, released in May 2004. The programs were developed independently, through which new functions can be added to WordPress.
Then, in February 2005, they added the ability to manage themes. The vast majority of themes and plugins have been (and are) being created by WordPress users themselves.
WordPress history from 2005 to 2007
According to Mullenweg’s Wikipedia page, version 1.5, released in February 2005, has received more than 900,000 downloads. In 2005, WordPress 1.5 version had more than 900,000 downloads. This is also the year wordpress.com was born to create a free blog for everyone.
By 2006, WordPress had 1,545,703 downloads. 2007 hit 3,816,965 downloads! Regarding plugins, there were a total of 191,567 downloads out of a total of 371 plugins in 2006. One year later (2007), there were 2,845,884 downloads in 1,384 plugins, a 15-fold increase!
The boom wordPress history
In 2009
Released in 2007, version 2.1 brings a new user interface that automatically saves articles and checks for spelling errors. Widgets, improved atom feed, and various speed optimizations were soon followed. In 2009, WordPress proudly announced the ability to automatically upgrade, built-in plugin installation, sticky posts, comments threaded comments/comment paging/replies, as well as there’s a new API, bulk management, and inline documents.
In 2010
Custom post types, custom menu management capabilities, and new APIs for custom headers and backgrounds, were introduced in 2010 along with the ability to manage multiple pages web (also known as multisite). Since then, users have seen more post formatting, an admin bar, welcome messages, feature suggestions, a customizer and theme preview, a file upload manager, and so much more …
In 2018
On December 6, 2018, WordPress launched version 5.0. The major improvement, is introducing a Block Editor called Gutenberg that customizes a richer and more complex post layout. There has been a lot of controversy about Gutenberg’s launch. It includes a separate movement coming from many programmers who didn’t want to use the feature.
According to 2018 statistics, WordPress.com has hosted around 37.5 million websites, and that number is probably still growing. It’s available anywhere and it supports dozens of languages. There is a free plan, and some low-cost, and the business and e-commerce plans have reasonable prices.
More than 60 million websites, including 33.6% of the top 10 million websites as of April 2019, use WordPress figures from Wikipedia. In other applications, such as pervasive display systems, WordPress has also been used.
From 2020 to 2022
As of January 2020, WordPress.org has 55,487 plugins available. Each theme offers custom functions and features that allow users to tailor their website to their specific needs. For example, customizations range from SEO to the client portal used, viewing logged-in users’ private information, content management systems,v.v.
Not all available plugins always come with upgrades. As a result, they may not work properly or may not work. Most of the plugins are available through WordPress itself, by downloading and installing files manually via FTP or through the WordPress dashboard.
From 2022 to 2024
2022 Focus on Full Site Editing (FSE): WordPress continued its focus on refining the Full Site Editing experience, which allows users to edit all aspects of their website using blocks. Version 5.9, named after Josephine Baker, introduced more site editing blocks, and numerous themes began offering enhanced site editing experiences based on the block editor.
2023:
- FSE Out of Beta: WordPress 6.2, named Eric Dolphy, marked a significant milestone as the Full Site Editing feature came out of beta. This meant that the feature was considered stable and ready for widespread use. A new template browsing experience was added, making it easier for users to create custom layouts without coding. The “distraction-free writing” mode was also re-introduced.
- Version 6.3 (Lionel Hampton): This version further improved the site editing experience with additional features and enhancements.
- Version 6.4 (Shirley Horn): Released in November, this version continued the trend of refining FSE and introducing new features.
2024:
- Version 6.5 (Regina Carter): Released in April, this version further refined and expanded the features and functionality of WordPress (like AVIF format image).
What’s the future of WordPress?
“WordPress powers 43.4% of all websites as their CMS. Around 474 million websites are built on WordPress. WordPress dominates the CMS market with a 62.8% share.” – Statistic from WPZoom.
So where did WordPress get such success? With over 60,000 free plugins, and 30,000 free themes available in the library, WordPress has truly gone beyond a basic CMS. It’s a system capable of powering a wide range of purposes!
What will the future of WordPress be like? The best way to answer this question is probably to listen to what Matt Mullenweg said: “I see the future of WordPress as a web operating system”. Limited only by the imagination of its users and developers, WordPress has a very, very bright future!
Popular WordPress Themes
Eduma – Education WordPress Theme

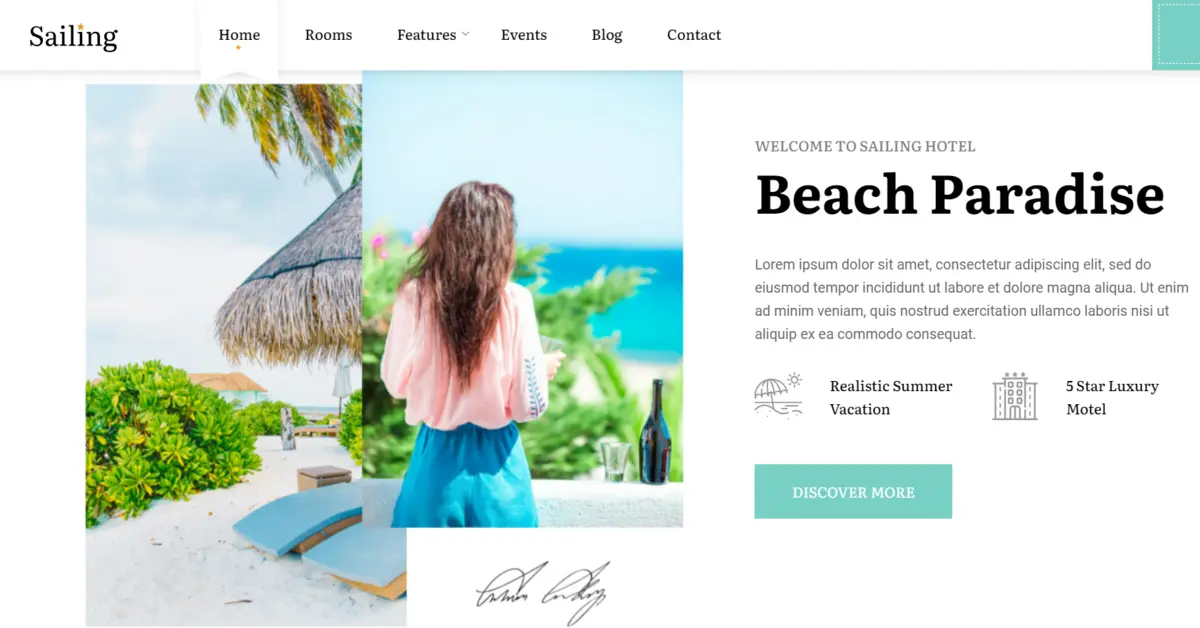
Sailing – Hotel WordPress Theme
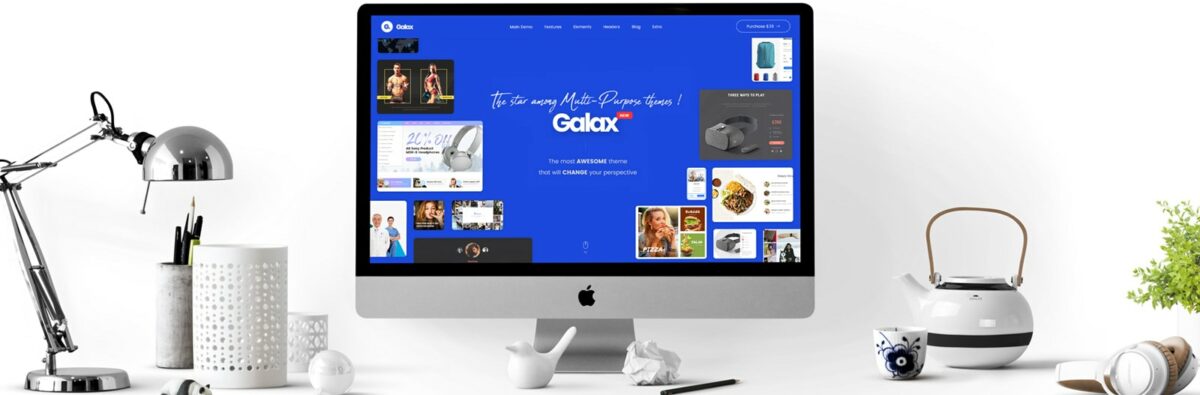
Galax – Multi-Purpose WordPress Theme
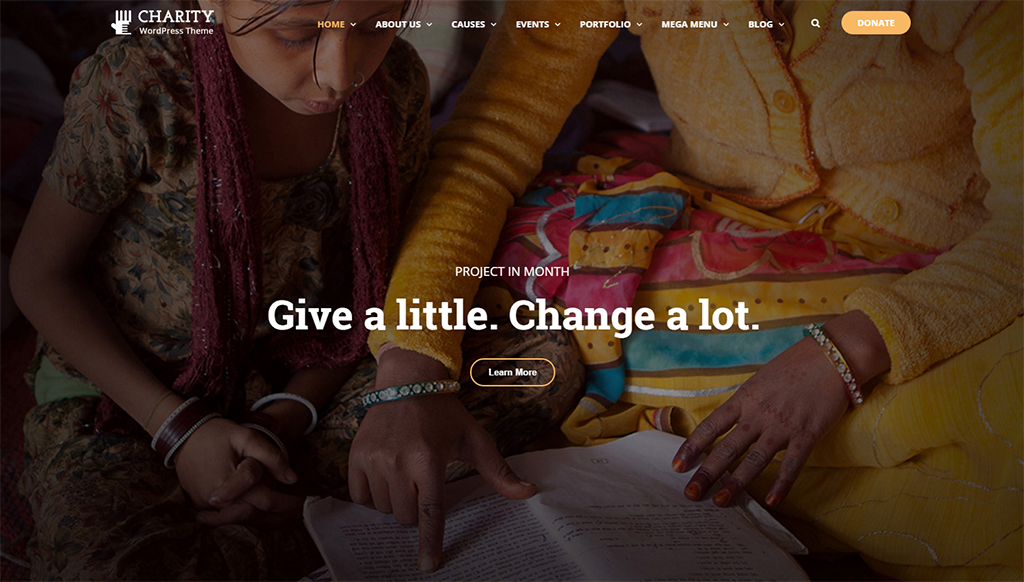
Charitix – Nonprofit Charity WordPress Themes
Read More: How to Choose the Best WordPress Hosting Providers
Contact US | ThimPress:
Website: https://thimpress.com/
Fanpage: https://www.facebook.com/ThimPress
YouTube: https://www.youtube.com/c/ThimPressDesign
Twitter (X): https://x.com/thimpress_com



